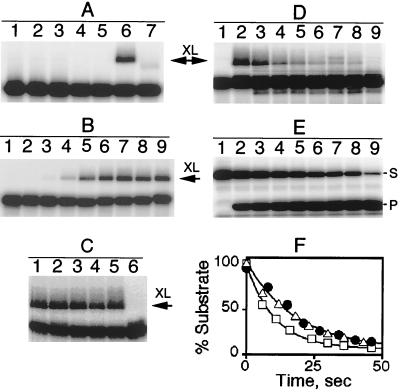
Figure 1.
Crosslinking of pre-tRNA and RNase P holoenzyme reconstituted with AzP-labeled S49C P protein. The RNase P⋅pre-tRNA complex was formed by incubating 32P-labeled pre-tRNA (5–10 nM pTR14 RNA) and 0.4 μM holoenzyme at 37°C in 50 mM Mes-Tris buffer, pH 6.0, 5 mM CaCl2. Samples were exposed to UV light (312 nm) for 1 min. The crosslinked (XL) products were separated on 15% SDS/PAGE and visualized by using a PhosphorImager. (A) Lane 1, pre-tRNA alone; lane 2, pre-tRNA and P RNA; lane 3, pre-tRNA and holoenzyme; lane 4, pre-tRNA and holoenzyme reconstituted with S49C P protein; lanes 5–7, pre-tRNA and holoenzyme reconstituted with AzP-labeled S49C P protein, no irradiation (lane 5), 1-min irradiation (lane 6), and irradiation followed by proteinase K digestion (five units at 37°C for 20 min) (lane 7). (B) Crosslinking depends on the length of the leader. Lane 1, mature tRNA; lanes 2–9, pre-tRNA substrates with a leader sequence of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, and 14 nt, respectively. (C) RNA specificity of crosslinks. pTR14 and holoenzyme reconstituted with AzP-S49C P protein was irradiated in the absence of competitor (lane 1), or in the presence of 5 μM mature tRNA (lane 2), 5 μM 5′ leader RNA (lane 3), 250 μg/ml of poly G RNA (lane 4), 250 μg/ml of poly C RNA (lane 5), and 2 μM pTR14 RNA (lane 6) as competitors. Only the substrate effectively inhibits formation of the crosslink. (D) Cleavage of the crosslinked pTR14/holoenzyme complex. The cleavage of pTR14 substrate crosslinked to AzP-S49C RNase P was initiated by the addition of MgCl2 (10 mM final concentration) and unlabeled pTR14 substrate (10 μM final concentration) to inhibit the activity of the uncrosslinked RNase P. The reaction was incubated at 37°C, and a 5-μl aliquot was quenched at defined times by the addition of SDS sample buffer. The crosslinked pre-tRNA (XL) and free pre-tRNA were separated on a 15% SDS/PAGE gel and quantitated by using a PhosphorImager. Lanes 1 and 2, 32P-labeled pTR14 and holoenzyme reconstituted with AzP-S49C P protein before and after UV irradiation; lanes 3–9, 8, 15, 21, 27, 34, 40, and 300 sec, respectively, after the addition of MgCl2. (E) Single turnover cleavage of pTR14 catalyzed by RNase P reconstituted with unmodified S49C P protein. 32P-labeled pre-tRNA (10 nM pTR14) was incubated with a saturating concentration (0.4 μM) of RNase P at 37°C in 50 mM Mes, 50 mM Tris, pH 6.0, 5 mM CaCl2, and the cleavage reaction was initiated by the addition of MgCl2 (10 mM final concentration). Pre-tRNA (S) and the 5′ leader sequence (P) were separated on a 15% SDS/PAGE gel and quantitated by using a PhosphorImager. Lane 1, 32P-labeled pTR14 and holoenzyme before addition of MgCl2; lanes 2–9, 6, 12, 18, 23, 30, 36, 43, and 314 sec, respectively, after the addition of MgCl2. (F) The percent substrate as a function of time is plotted for the single turnover cleavage of pTR14 catalyzed by wild-type RNase P (□), RNase P reconstituted with S49C P protein (▵), and pTR14 crosslinked to RNase P reconstituted with AzP-S49C P protein (•). The data are fit to a single exponential decay by using the Kaleidagraph (Synergy software) curve-fitting program; the fitted rate constant and endpoint are 0.09 ± 0.01 s−1 and 6 ± 2% for wild-type RNase P and 0.05 ± 0.01 s−1 and 5 ± 2% for either RNase P reconstituted with S49C P protein or pTR14 crosslinked to RNase P reconstituted with AzP-S49C P protein.