Table 2.
Optimization of Reaction Conditionsa
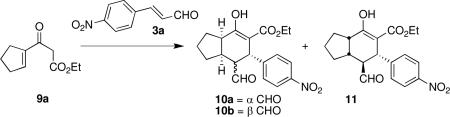 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | mol % 1a | additive | solvent | time (h) | % conversionb | dr (10:11)b | ee (10a)c | ee (10b)c |
| 1 | 20 | PhCO2H | toluene | 168 | 5 | 80:20 | nd | nd |
| 2 | 20 | PhCO2H | Et2O | 168 | <1 | nd | nd | nd |
| 3 | 20 | PhCO2H | THF | 168 | 0 | nd | nd | nd |
| 4 | 20 | PhCO2H | MeCN | 168 | 32 | 93:7 | 99 | 99 |
| 5 | 20 | PhCO2H | CF3CH2OH | 2 | 12 | 89:11 | nd | nd |
| 6 | 20 | PhCO2H | CF3CH2OH | 41 | 17 | 91:9 | 99 | 99 |
| 7 | 20 | -- | CF3CH2OH | 17 | 85 | 90:10 | 99 | 99 |
| 8 | 10 | -- | CF3CH2OH | 17 | 87 | 91:9 | 99 | 99 |
| 9 | 5 | -- | CF3CH2OH | 17 | 80 | 91:9 | 99 | 99 |
| 10 | 1 | -- | CF3CH2OH | 88 | 25 | 88:12 | 99 | 99 |
| 11d | 5 | -- | CF3CH2OH | 46 | 76 | 92 : 8 | 99 | 99 |
Reaction conditions: 3a (1 equiv), 9a (1 equiv), 1a, additive (20 mol %), solvent (0.3 M), rt.
Determined by 1H NMR of crude reaction mixture.
Determined by chiral HPLC.
Reaction run at 0 °C.
