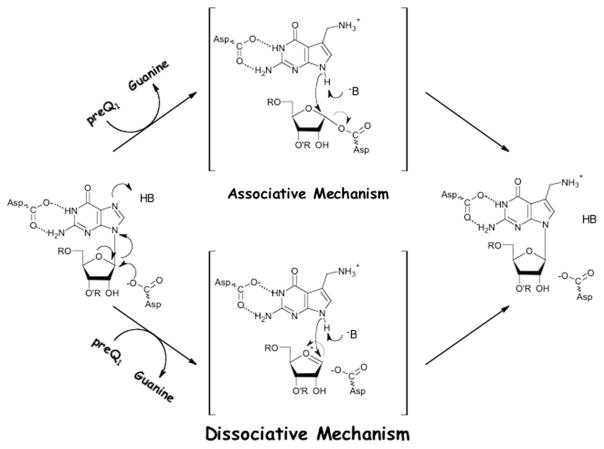
Fig. 4.
Two potential chemical mechanisms for the TGT reaction involving two aspartates. In the “associative mechanism,” an aspartate acts as a nucleophile to displace guanine. In the “dissociative mechanism,” an aspartate stabilizes an oxocarbenium ion intermediate. In both mechanisms, a general acid (either enzymic or water) serves as a proton donor to facilitate the departure of guanine.