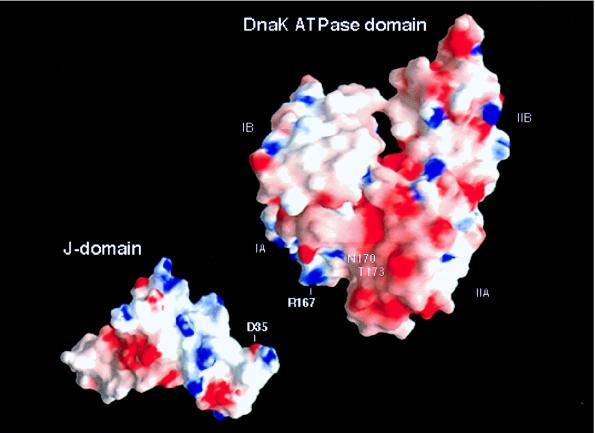
Figure 4.
Electrostatic surface potentials of the ATPase domain of DnaK (PDB ID code 1DKG) (24) with A167 modeled to R167 by using the program o (25) and the J-domain of DnaJ (PDB ID code 1XBL) (11). Areas of positive and negative charges are colored blue and red, respectively. The electrostatic surface potentials were calculated and displayed by using the program grasp (26). Residue 167 in the original PDB file is Ala instead of Arg (commonly used if the density for a residue is hard to define). The difficulty in identifying the density of residue 167 indicates that this residue is disordered. The high mobility of this residue suggests that residue 167 is not involved in intramolecular interaction within the DnaK ATPase domain but could be involved in intermolecular interaction with the D35 located in the J-domain. The groove between the IA and IIA subdomains of the ATPase domain has a patch of negative electrostatic surface potential, which is likely a potential binding pocket for the exposed positively charged residues on helix II of the DnaJ J-domain.