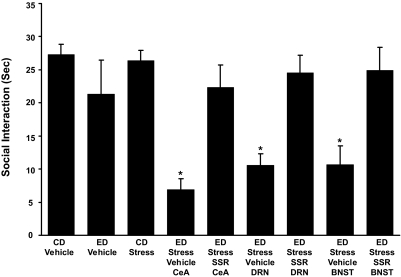
Fig. 8.
Microinjection of CRF-1 receptor antagonist (SSR) into the CeA, DRN, or d-BNST before restraint stress prevents sensitization of ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior. The CRF-1 receptor antagonist SSR125543 (SSR; 10 μg/0.5 μl) was microinjected into the CeA, DRN, or the d-BNST 15 min before the two weekly 60-min restraint stresses before exposure to 5 days of 4.5% ED (see Fig. 1 for protocol). Social interaction was measured 5 to 6 h after the ethanol diet removal. The anxiogenic effect of stress on ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety was blocked by the SSR125543 microinjected in the selected brain sites. The number of rats for each group is listed in Table 1, part 6. For the CD-vehicle and ED-vehicle groups, vehicle was administered into each of the brain sites (n = 3–6 for each site). The vehicle data for each of these controls were combined because a significant change across sites was not observed. No significant effect on social interaction (P > 0.05) was observed during ethanol withdrawal when the CD-vehicle group was compared with the ED-vehicle group. A representation of brain site at which CRF injections were aimed for each site is presented in Supplemental Material. *, P < 0.001 compared with the CD-vehicle, ED-vehicle, and CD stress groups as well as the groups that received the CRF-1 receptor antagonist before the repeated stresses. [F(8, 75) = 7.385, *, P < 0.001].