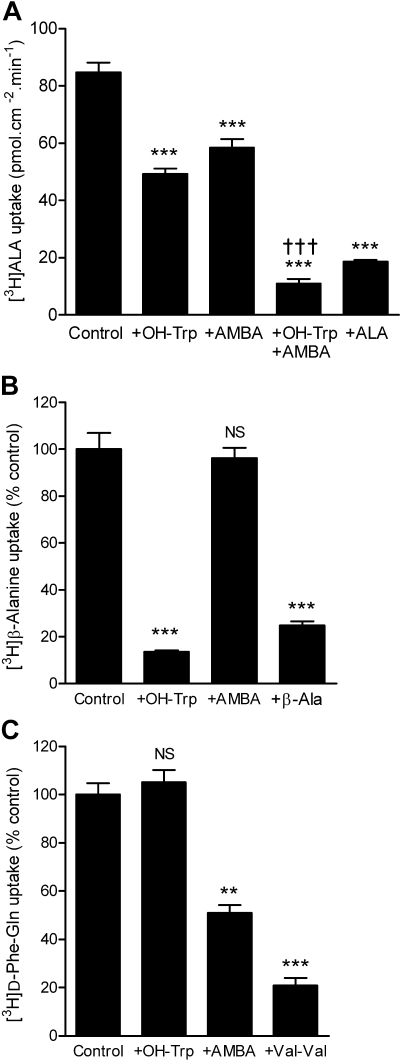
Fig. 5.
Both PAT1 and PepT1 mediate ALA uptake across the intestinal brush-border membrane. A, apical uptake of [3H]ALA (100 μM) was measured at apical pH 5.5 and basolateral pH 7.4 in the presence and absence of excess ALA (20 mM), the PAT1 inhibitor OH-Trp (20 mM), and/or the PepT1 inhibitor AMBA (30 mM). ***, p < 0.001 versus control; †††, p < 0.001 versus either +AMBA or +OH-Trp. B, apical uptake of the PAT1 substrate [3H]-β-alanine (β-Ala) (100 μM) in the presence of the PAT1 inhibitor OH-Trp (20 mM), the PepT1 inhibitor AMBA (30 mM), or unlabeled β-alanine (30 mM). ***, p < 0.001; NS, p > 0.05, versus control. C, apical uptake of the PepT1 substrate [3H]-d-Phe-Gln (100 μM) in the presence of the PAT1 inhibitor OH-Trp (20 mM), the PepT1 inhibitor AMBA (30 mM), or the dipeptide Val-Val (30 mM). ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; NS, p > 0.05, versus control.