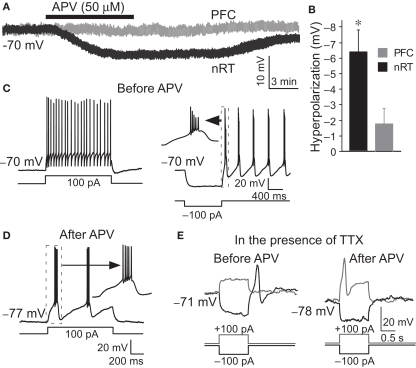
Figure 1.
APV hyperpolarized nRT GABAergic neurons and changed their firing mode. (A) 50 μM APV hyperpolarized nRT GABAergic neurons, but not PFC pyramidal neurons. (B) Group data show quantification of APV-induced hyperpolarization in nRT and PFC. (C) Before APV application, a depolarizing pulse induced tonic spiking (left panel), whereas hyperpolarization induced a rebound burst (right panel). (D) In the presence of APV, the same depolarizing current induced bursting activity. (E) In 0.5 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX), before APV application, hyperpolarizing pulse induced a rebound calcium spike; a depolarizing pulse did not induce active response in nRT neurons (left panel). After APV was applied, a depolarizing pulse induced a calcium spike (right panel).