Figure 4.
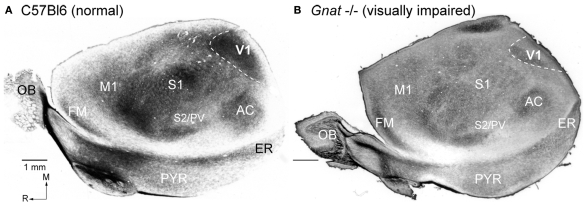
Myeloarchitecture of the Cortex in C57Bl6 and Gnat−/− Mice. Digital images of flattened cortex sectioned tangential to the pial surface and processed for myelin, illustrating some of the cortical area borders in C57Bl6 (A) and Gnat−/− (B) mice. Although cortical field boundaries are determined from the entire series of sections, many of the boundaries of cortical fields can often be observed on a single section. The primary visual area (V1) is the darkly myelinated region at the caudal pole of cortex (dashed white lines). In the Gnat−/− mouse, the rostral boundaries of V1 are clearly visible, but in this particular section the caudal boundaries are not as clear. However, at the caudal pole the dense myelination of layer 4, indicative of area 17 is clearly visible. The primary somatosensory area (S1) is a darkly myelinated region that is interrupted by myelin light regions separating major body parts. Auditory cortex (AC) is a darkly myelinated oval in the temporal pole of the cortex and is co-extensive with several auditory areas including the primary auditory area (A1) and the anterior auditory field (AAF). M1 is a moderately myelinated area just rostral to S1. Medial is to the top and rostral is to the left in all images. Scale bars = 1 mm.