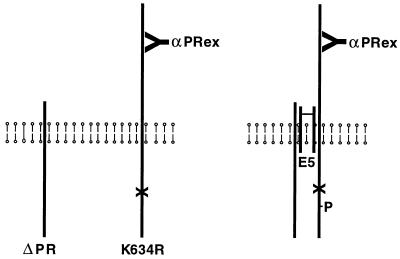
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of coimmunoprecipitation experiments. The vertical lines represent the full-length kinase-negative receptor (K634R), the truncated kinase-active receptor (ΔPR), and a dimer of the E5 protein traversing the cell membrane. αPRex antibody, which specifically recognizes the extracellular domain of the full-length receptor, also is shown. (Left) Receptors existing independently in cells in the absence of the E5 protein. (Right) Heteromeric receptor complex held together by the E5 dimer. (X) represents the mutation in K634R that destroys kinase activity, and (P) represents phosphate on the kinase-negative receptor trans-phosphorylated in response to the E5 protein.