Figure 2. Induction of TA-specific CTL responses by TA-specific mAb-based immunotherapy.
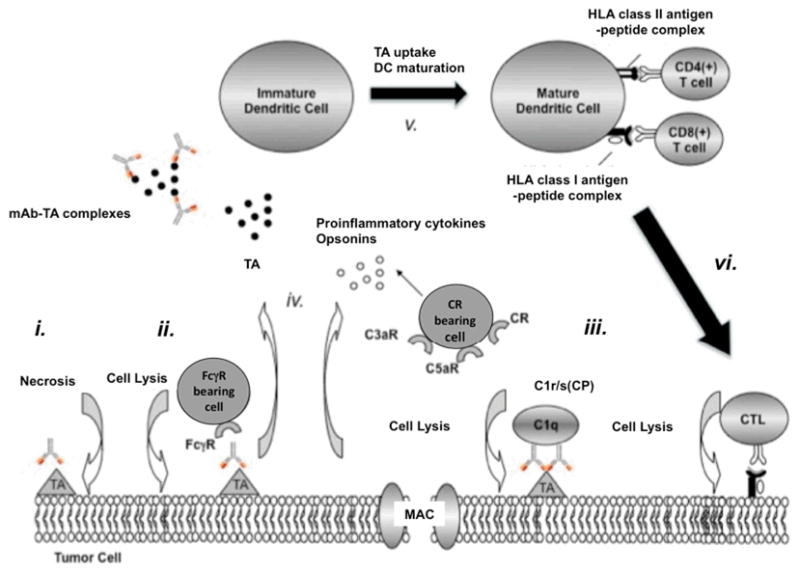
TA-specific mAb may enhance the generation and promote the survival of TA-specific CTL via several mechanisms. TA-specific mAb may (i) induce tumor cell death or activate (ii) ADCC and (iii) CDC. The latter results in 1) the formation of the lytic membrane-attack complex (MAC); 2) the generation of opsonins (C3b), and 3) the release of the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. The culmination of the above events (i, ii, iii) leads to the release of Th1 cytokines, (iv) the formation of TA-specific mAb-TA complexes and (v) the uptake of TA and TA-specific mAb-TA complexes by APC. Ultimately, mature DC present processed TA to CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells, and promote the generation of (vi) TA-specific CTL.
