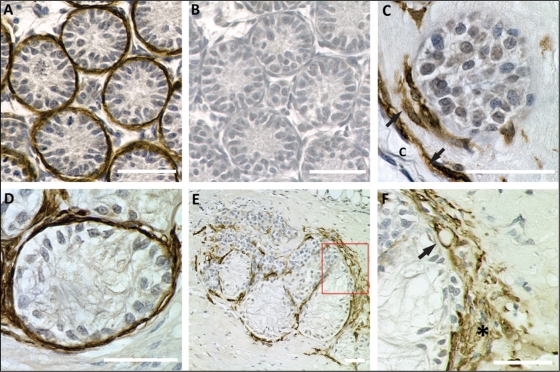
Figure 7.
Development of peritubular myoid cells in xenografts.
Xenografts were stained for α-smooth muscle actin (SMA, brown precipitate), a myoid and smooth muscle cell marker. Scale bars = 50 µm. (A) Positive control. A representative cross-section from a 7-day-old rat testis. Immature testicular cords are surrounded by peritubular myoid cell. (B) The same tubules as shown in A in an adjacent section that was incubated with secondary antibody only. No staining is visible in the control section. (C) Sertoli cell cord in a xenograft after 1 week. The cord is partly surrounded by peritubular myoid cells (arrow). The connective tissue capsule (c) next to the cord is aligned by myoid cells (arrow). (D) After 4 weeks, Sertoli cell tubules are surrounded by peritubular myoid cells, as indicated by positive staining for SMA. (E) Cluster of Sertoli cell tubules and inter-tubular compartment in a xenograft after 12 weeks. Peritubular myoid cells are located around Sertoli cell tubules. Single myoid cells or small groups are located within the inter-tubular compartment. (F) Higher magnification of the boxed area in E. The connective tissue capsule is covered with multi-layered myoid cells (asterisk). A SMA-positive vascular wall cell, indicating vascularization, is shown (arrow).