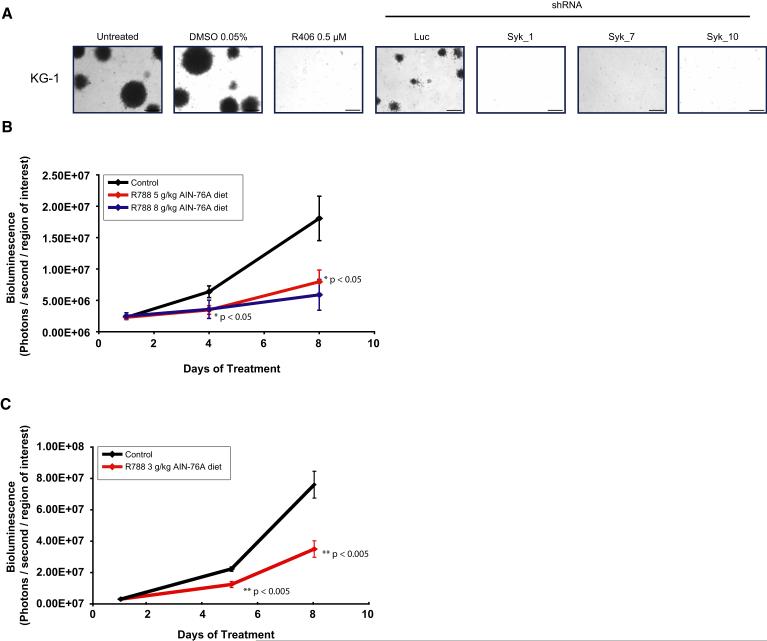
Figure 5. R406 has in vivo activity in AML.
(A) The ability of KG-1 to form colonies in methylcellulose with R406 and multiple shRNAs directed against SYK was assessed. Both chemical and genetic inhibition of Syk abrogate colony formation in KG-1. The scale bar equals 1 mm.
(B) KG-1 luciferase positive xenografts were established in NOG mice. Mice were treated with placebo (n=4), food impregnated with 5g R788 / kg AIN-76A food (n=5), and food impregnated with 8g/kg AIN-76A food (n=3) for 8 days. Mice treated with R788 had a significant difference in tumor burden compared to those treated with placebo. Serial in vivo BLI was used to assess disease burden, and data plotted as the mean ±SEM for each group. One way ANOVA analysis with Tukey post-test was used to determine the significance of all pairwise comparisons.
(C) A syngeneic, luciferase positive mouse model of MLL-AF9 AML was established in C57BL/6:TyrC/C mice. Mice were treated with placebo (n=10) or food impregnated with 3g R788 / kg AIN-76 food (n=10) for 8 days. Serial in vivo BLI was used to assess disease burden and plotted as mean ±SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using Student’s t-test.