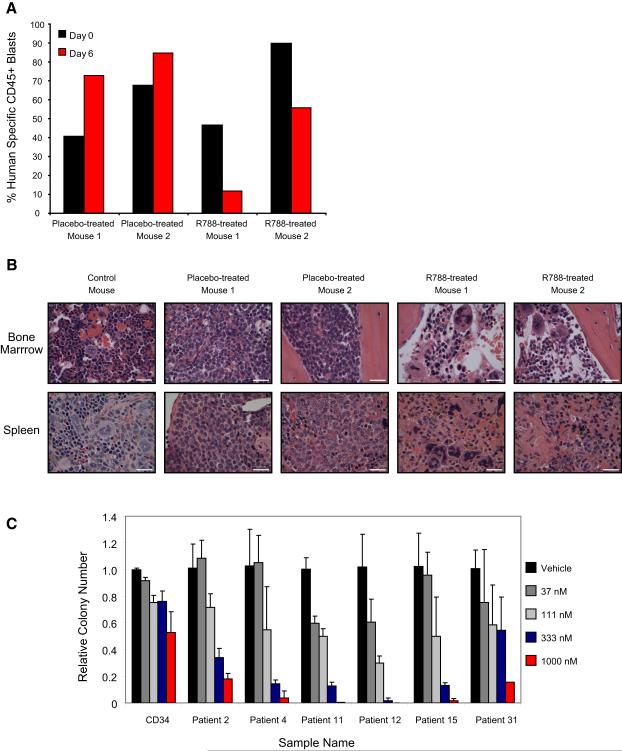
Figure 7. Primary AML is responsive to Syk inhibition in an orthotopic model.
(A) A primary AML (Patient 11) orthotopic xenograft was established in NOG mice. Six days after initiation of treatment with food containing 5g R788/kg AIN-76 rodent diet, the AML blast percentage, measured by percentage of human specific CD45+ cells in peripheral blood, continued to increase in the placebo-treated mice but decreased in the R788-treated mice.
(B) Histopathology studies of bone marrow in R788-treated versus placebo-treated animals reveal near resolution of AML infiltration with areas of necrosis and areas of recovering marrow identified. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of spleen reveals areas of leukemic infiltration and extramedullary hematopoiesis in placebo-treated mice and near resolution of AML infiltration in the R788-treated animals. Images were acquired with an Olympus BX41 microscope, 1000X magnification under oil, and Qcapture software. The scale bar equals 25 μm.
(C) The ability of normal CD34 myeloid progenitor cells and primary patient AML blasts to form colonies in methylcellulose with R406 was assessed. Colony formation was assessed in duplicate and colonies per 4 cm2 counted and displayed relative to control cells. Error bars depict mean ± SD across 4 ratios of dose response to vehicle. Primary patient AML blasts were more sensitive to the effects of R406 than were normal myeloid progenitors.