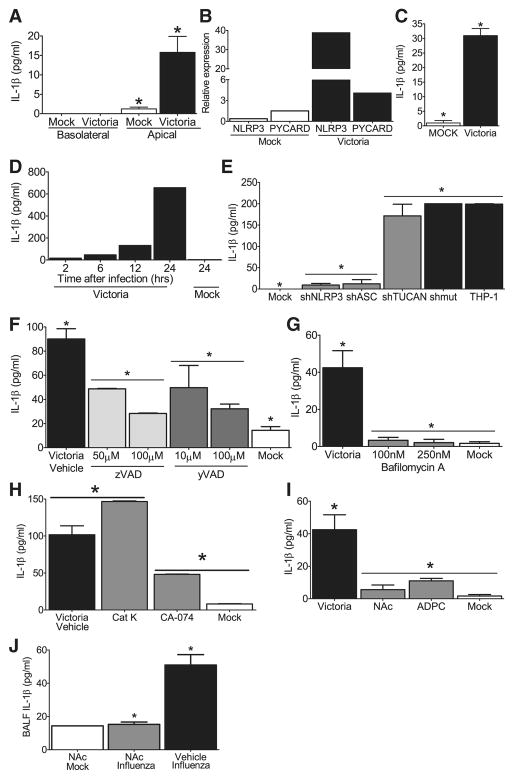
Figure 5. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in response to influenza virus is dependent upon lysosomal maturation and ROS production in human cells.
(A) Depiction of the primary ciliated human airway epithelial (HAE) cultures which were infected with the human pathogenic influenza virus A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2; MOI = 1). Supernatants are collected from the apical and basolateral surfaces. (B) Robust viral replication was observed over the course of the HAE infection. (C) IL-1β levels were detected in the apical, but not basolateral, compartment 48 hours post-infection. (D) Human nasal airway epithelial cell lines (JME) were infected with A/Victoria/3/75 (MOI=1) and increased NLRP3 and ASC mRNA expression was observed. Data was normalized to 18s and compared to the expression in similarly treated human type II alveolar epithelial-like cell lines (A549). (E) Increased IL-1β protein was observed 24 hours post-infection in the cell free supernatant from the JMEs. (F) Human THP-1 monocyte cell lines were infected with A/Victoria/3/75 (MOI=5) and increased IL-1β levels were observed in the supernatant over a 24hr time course. (G–I) Influenza mediated IL-1β generation is dependent upon the NLRP3 inflammasome in human monocytes. (G) Human THP-1 cells were infected with lentivirus containing shRNA for ASC, NLRP3 or TUCAN (shASC, shNLRP3 or shTUCAN) or a mutated sh target sequence (shmut). Cell free supernatants were collected 24 hours post-infection (MOI=1). Influenza induced NLRP3- and ASC- dependent increase in IL-1β (*p<0.05), which was independent of TUCAN. (H) The general caspase inhibitor ZVAD-CHO and (I) the caspase-1 specific inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO, both inhibited IL-1β release in a dose-dependent manner (*p<0.05). (J–L) Influenza mediated IL-1β maturation requires lysosomal maturation and ROS production in THP-1. IL-1β release during influenza infection (MOI=5) was attenuated following treatment with (J) the lysosome inhibitor bafilomycin A (100–250nM), (K) the cathepsin B inhibitor CA-074-Me (50μM), and (L) the ROS inhibitors APDC (100μM) and NAc (50μM)(*p<0.05). (M) Treatment with the ROS inhibitor NAc (250mg/kg) inhibits influenza mediated IL-1β release in vivo (*p<0.05). NAc Mock, n=1; NAc Influenza, n=5, Vehicle Influenza, n=3.