Figure 1. Endothelial ICAM-1 Is Clustered by Chemokine-Stimulated LFA-1 in T Cells Crawling under Shear Flow.
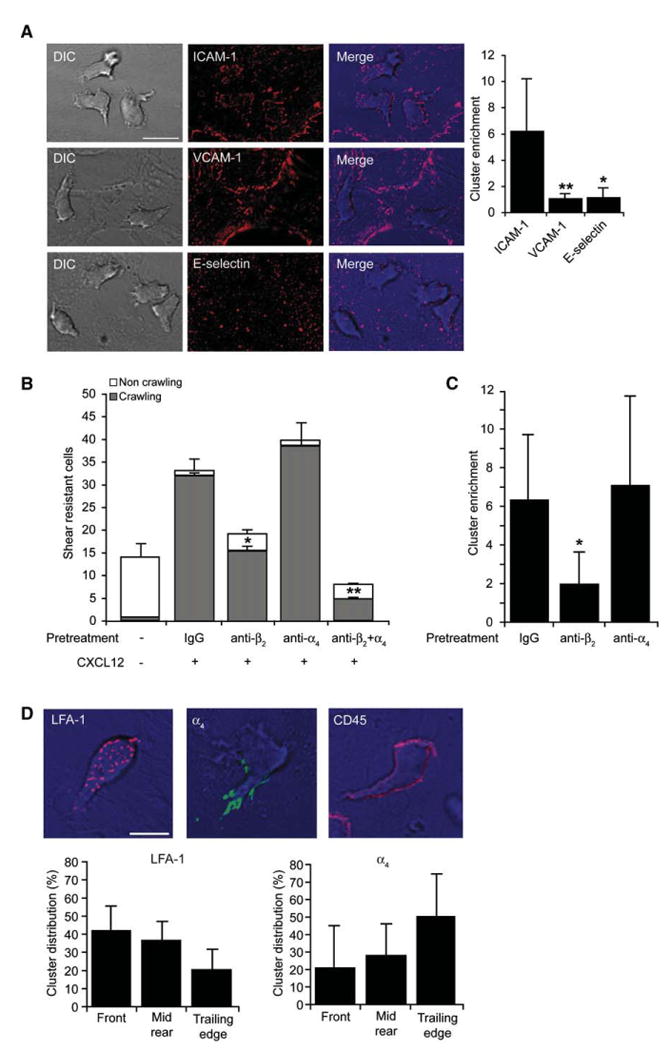
(A) Human peripheral blood T cells accumulated for 1 min on activated HUVEC overlaid with CXCL12 were subjected to shear stress of 5 dyn/cm2. Actively crawling lymphocytes (>90% of originally accumulated T cells) were fixed 7 min after accumulation and stained with mAbs to ICAM-1, VCAM-1, or E-selectin. Scale bar represents 10 μm. Right graph: cluster enrichment in areas underneath crawling T cells versus areas proximal to these cells. Background staining is shown in Figure S2B. Values are the mean ± SD of 20 crawling T cells in each experimental group. *p < 0.00001; **p < 0.00001.
(B) Effects of blocking T cell LFA-1 and α4 integrins (with TS1.18 and HP1/2, respectively) on T cell arrest and crawling on activated HUVEC overlaid with CXCL12. Values represent the mean ± range of two fields in each experimental group and results are representative of three independent experiments. *p < 0.035; **p < 0.006 for the indicated crawling fractions compared to control mAb-treated T cells.
(C) Enrichment of ICAM-1 clusters under T cells treated with control IgG-, β2-, or α4-blocking mAbs measured as in (A). *p < 0.0001.
(D) Crawling T cells were fixed and stained for LFA-1 (red), β4 integrins (green), or CD45 (red). Scale bar represents 6 μm. Lower panels depict the distribution of LFA-1 or β4 integrin clusters in different compartments of crawling T cells. Values are the mean ± SD of 20 crawling T cells in each experimental group.
