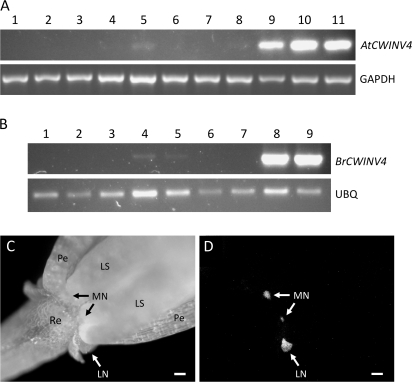
Fig. 1.
CWINV4 is highly expressed in nectaries. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to examine the expression profiles of AtCWINV4 (A) and an orthologue from Brassica rapa (B; BrCWINV4, accession number GQ146458). The tissues examined in (A) included: (1) petal; (2) sepal; (3) rosette leaf; (4) stamen; (5) pistil; (6) root; (7) internode shoot; (8) silique; (9) mature median nectaries (Stage 14–15); (10) immature lateral nectaries (Stage 11–12); and, (11) mature lateral nectaries (Stage 14–15). (B) Tissues included: (1) petal; (2) sepal; (3) leaf; (4) stamen; (5) pistil; (6) root; (7) stem; (8) mature median nectaries; and (9) mature lateral nectaries. GAPDH (At3g04120) and a B. rapa ubiquitin gene (BrUBQ, accession number GR719937) were used as constitutively expressed controls. All B. rapa floral tissues examined were from the equivalent of Stage 14–15 Arabidopsis flowers. The images shown are the results obtained after 27 cycles of RT-PCR. (C) Bright field image of Stage 15 Arabidopsis flower expressing an AtCWINV4:GFP fusion, under control of the native AtCWINV4 promoter, and (D) GFP fluorescence derived from same flower. Sepals were removed prior to imaging. Re, receptacle; Pe, petal; LS, long stamen; MN, median nectary; LN, lateral nectary; scale bars, 100 μm.