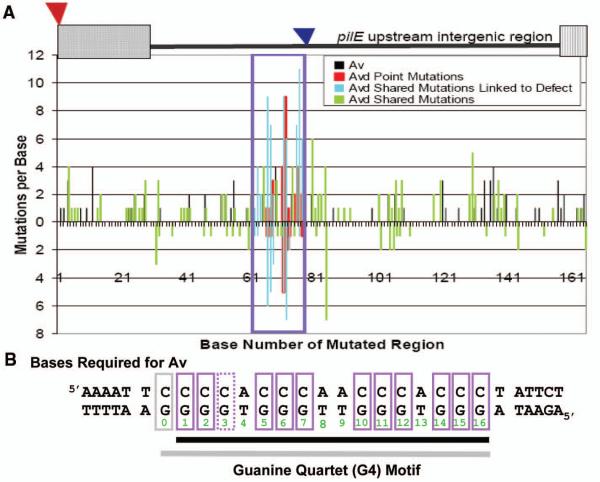
Figure 1. Identification of a DNA sequence in the intergenic region upstream of pilE required for gonococcal pilin Av.
A. Mutational Spectrum of Genetic Screens: A cartoon of the mutagenized region from the transposon insertion (red triangle) that has no affect on pilin Av (13) to 165bps downstream showing the location of the previously identified Av-disrupting transposons (blue triangle) (11, 13). X-axis indicates base number while y-axis indicates number of mutations isolated per base. Screen #1 (bottom axis) represents 103 Avd mutants (only mutants with mutations <9 are shown) (Table S1A). Screen #2 (top axis) represents 204 Av transformants and 106 Avd mutants (only mutants with mutations <17 are shown) (Table S1B). The region linked to the Avd phenotype is boxed. Bars indicate mutations that allow Av (black), single mutations that cause an Avd phenotype (red), and Avd mutants that have mutations within the boxed region (blue) but have mutations elsewhere (green). B. Bases required for pilin Av: Mutation of individual purple boxed bps result in an Avd phenotype. Solid purple boxes indicate a complete block of pilin Av while the G-3 mutant shows residual activity (Fig. S2). The DNA element on the bottom strand forms a guanine quartet (G4) motif (black underlined bases 1-16), when G-3 is mutated, the alternative G4 using G-0 (grey box) is shown underlined in grey.