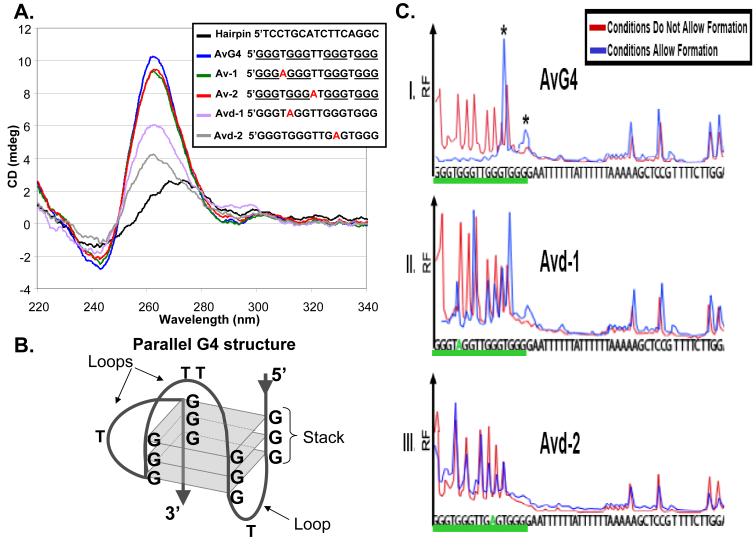
Figure 2. Analysis of G4 structure formation in vitro.
A. Circular dichroism (CD) spectrometry: The Hairpin oligonucleotide forms a double stranded DNA molecule producing a B-DNA CD spectrum (25). The AvG4 oligonucleotide has the pilE G4 sequence that allows pilin Av, Av-1 and Av-2 oligonucleotides have A-T mutations that do not alter Av, and all produce parallel G4 structure CD spectrums (25). Avd-1 and Avd-2 oligonucleotides contain G-A transversions that block pilin Av and show altered CD spectrums. B. Parallel G4 structure: Three G-quartets (squares) in a parallel G4 configuration. C. Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) methylase protection assay: Formed G4 guanines are protected from DMS attack (26). Shown are representative electropherograms of a FAM-labeled 52bp oligonucleotide containing: I. The wild-type G4 sequence (AvG4 underlined), or II and III, two mutations that block pilin Av (Avd-1 and Avd-2, underlined). N=3. X-axis indicates the base and y-axis shows relative fluorescence (RF). Blue and red traces indicate G4 forming and non-forming conditions, respectively. Under G4 forming conditions, AvG4 forms two alternative G4 structures (5′GGGTGGGTTGGGTGGGG or 5‘GGGTGGGTTGGGTGGGG, guanines forming the structure are underlined, asterisks) while mutant oligonucleotides do not form the structure.