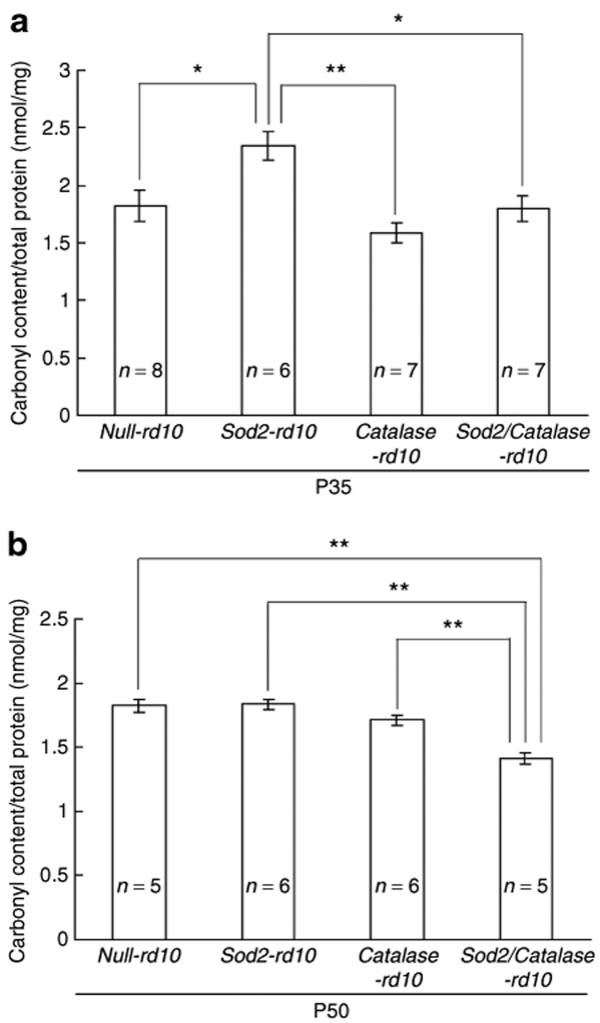
Figure 4.
Increased expression of Catalase and superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) significantly reduce carbonyl content in the retinas of postnatal day (P) 50 rd10+/+ mice. Starting at P10, the mothers of null-rd10+/+, Sod2-rd10+/+, Catalase-rd10+/+, and Sod2/Catalase-rd10+/+ mice and after weaning the mice themselves were treated with doxycycline. Mice were euthanized at P35 or P50 and protein carbonyl content was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of retinal homogenates. At P35, the mean (±SEM) carbonyl content per mg retinal protein was significantly greater in Sod2-rd10+/+ mice than null-rd10+/+, Catalase-rd10+/+, or Sod2/Catalase-rd10+/+ mice (a; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 by Tukey–Kramer test). At P50, the mean (±SEM) carbonyl content per mg retinal protein was significantly less in Sod2/Catalase-rd10+/+ mice compared to null-rd10+/+, Sod2-rd10+/+, or Catalase-rd10+/+ mice (b; **P < 0.01 by Tukey–Kramer test).