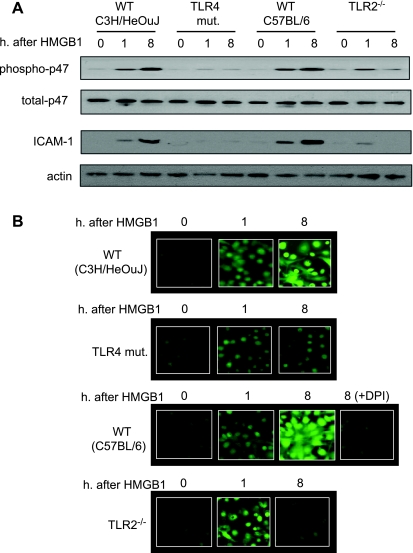
Fig. 6.
TLR4 and TLR2 sequentially mediate HS/R-induced activation of lung ECs. A: MLVECs were isolated from TLR4-mutant, TLR4 WT (C3H/HeOuJ), TLR2−/−, and TLR2 WT (C57BL/6) mice and incubated with recombinant HMGB1 (0.5 μg/ml) for 0 to 8 h; p47phox phosphorylation and ICAM-1 expression in the MLVECs were then assessed. Treatment with HMGB1 for 8 h exhibited a sustained activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and ICAM-1 expression in the WT MLVECs, but not in TLR4-mutant and TLR2−/− MLVECs. B: reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in live MLVECs. MLVECs that were cultured in 12-well cell culture plate were stained with the cell-permeable ROS detection reagent H2DFFDA in the concentration of 10 μM for 10 min. Cells were then washed with HBSS 3 times followed by incubation in the growth medium in the presence or absence of HMGB1 (0.5 μg/ml) for 8 h. The ROS production was then detected by fluorescence microscopy at different time points as indicated. In some experiments, the NAD(P)H oxidase-specific inhibitor diphenyleneiodonium (DPI) (100 μM) was added to the WT (C57BL/6) MLVECs immediately before the treatment of HMGB1 to specify the source of ROS. Blots are representative of at least 3 independent studies.