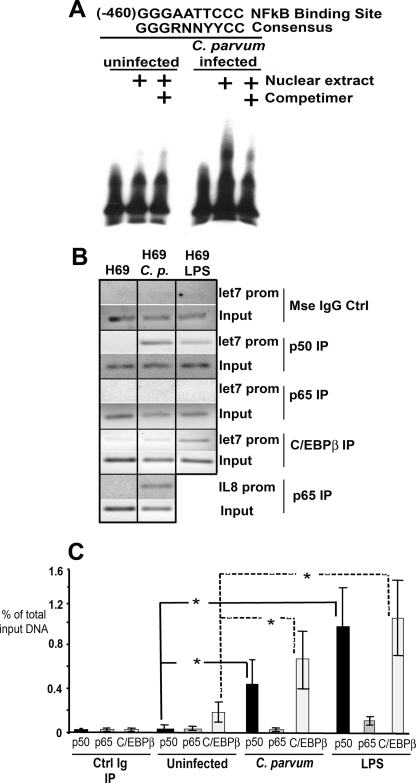
FIGURE 4.
Immune-associated transcription factors interact with the putative let-7i promoter following microbial stimulus. A, electrophoretic mobility shift assays were used to demonstrate interactions between nuclear factors and the let-7i promoter following infection. An oligonucleotide containing the proximal NFκB binding site did not shift when the nuclear extract from basal, uninfected cells was used. However, the same oligonucleotide demonstrated less mobility through the gel when the nuclear extract from C. parvum-infected cells was used. This interaction could be competed away using unlabeled oligonucleotide competimer. B, ChIP analysis demonstrated that both NFκB p50 (but not p65) and C/EBPβ interact with the let-7i promoter following microbial stimulus. ChIP analyses for the interleukin-8 promoter were performed as a positive control for p65 with both uninfected and C. parvum-infected H69 cells. C, quantitative PCR ChIP was also performed to verify the increased interaction between the let-7i promoter and the transcription factors NFκB p50 and C/EBPβ. A standard curve was generated using amplicons of a known copy number. The data are presented as the relative amount of the immunoprecipitated fraction compared with total input DNA. Data are represented as mean ± S.E. from four separate experiments. *, p < 0.05 compared with respective uninfected controls by ANOVA.