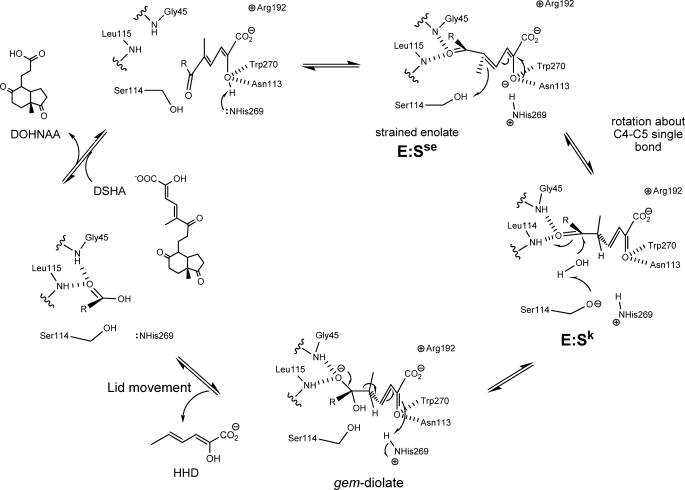
FIGURE 8.
Proposed mechanism of HsaD. Upon binding of the MCP, His269 deprotonates the hydroxyl at C-2, generating a strained enolate intermediate, E:Sse. Protonation of C-5 by Ser114 drives tautomerization of the substrate to generate a keto intermediate, E:Sk. Ser114 is positioned to activate water for attack at the C-6 carbonyl to form the gem-diolate. The collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate releases HHD, which triggers a conformational change in the lid domain and allows subsequent release of DOHNAA.