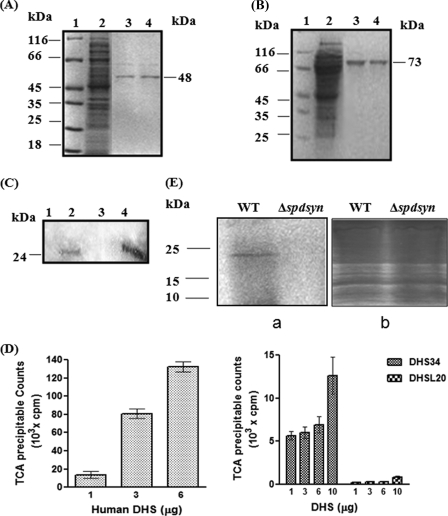
FIGURE 5.
Characterization of DHSL20 and DHS34 proteins. A, purification of DHSL20 protein on Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid affinity resin. Lane 1, molecular weight protein marker (MBI Fermentas); lane 2, flow-through; lanes 3 and 4, eluted fractions showing purified protein with buffer containing 300 mm imidazole. B, purification of DHS34 protein on Ni2+-NTA affinity resin. Lane 1, molecular weight marker; lane 2, flow-through; lanes 3 and 4, eluted fractions showing purified DHS34 protein with buffer containing 300 mm imidazole from the affinity column. C, identification of 3H-labeled deoxyhypusine-containing eIF5A product from DHS reaction mixture by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. Lane 1, DHS34 minus eIF5A; lane 2, DHS34 plus eIF5A; lane 3, human recombinant DHS minus eIF5A; lane 4, human recombinant DHS plus eIF5A. D, comparison of trichloroacetic acid-precipitable counts obtained in the DHS enzyme assay using different concentrations of recombinant enzymes, human DHS (hDHS), DHS34, or DHSL20. A DHS enzyme assay was performed as reported under “Experimental Procedures.” Results are mean ± S.D. of triplicate samples. E, in vivo metabolic labeling of 18-kDa protein in the wild type cells (WT) but not in the (Δspdsyn) mutant after culture with [1, 4-14C]putrescine. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue (b) and subsequently dried and exposed to autoradiography (a).