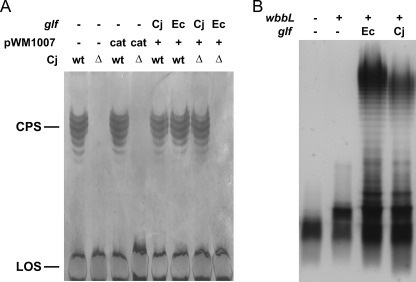
FIGURE 5.
C. jejuni glf gene complements CPS in C. jejuni Δglf strain and LPS in E. coli Δglf strain. A, separation of C. jejuni 11168 crude CPS preparations by 16.5% deoxycholate PAGE. Equivalent amounts of sample were loaded in each lane that originated from bacterial cell cultures adjusted to an absorbance (A600) of 3.0. Silver staining showed formation of CPS in the Cj-wt strain as well as Cj-wt with pMW1007/cat, pMW1007/Cj-glf, or pMW1007/Ec-glf plasmids. wt is wild type The C. jejuni 1439c (glf) knock-out strain (Cj-Δ) and the Cj-Δ strain with pMW1007/cat plasmid showed no CPS formation. Cj-Δ strain complemented with pMW1007/Cj-glf showed restoration of CPS production, and no CPS was observed in Cj-Δ complemented with pMW1007/Ec-glf. In all strains lipooligosaccharide (LOS) formation was not affected. B, LPS of E. coli strains derived from MFF1 were extracted after overnight growth and separated by SDS-PAGE. Equivalent amounts of sample were loaded in each lane that originated from bacterial cell cultures adjusted to an A600 of 0.45. Silver staining shows the production of a fast migrating band composed of lipid A core plus a GlcNAc residue (wbbL −, glf −); a band of higher molecular weight due to addition of an incomplete O antigen subunit to the lipid A core, which is only deficient of the Galf residue (wbbL +, glf −); and smooth LPS when both wbbL and either the E. coli or the C. jejuni glf are present (wbbL +, Ec-glf and wbbL +, Cj-glf), respectively.