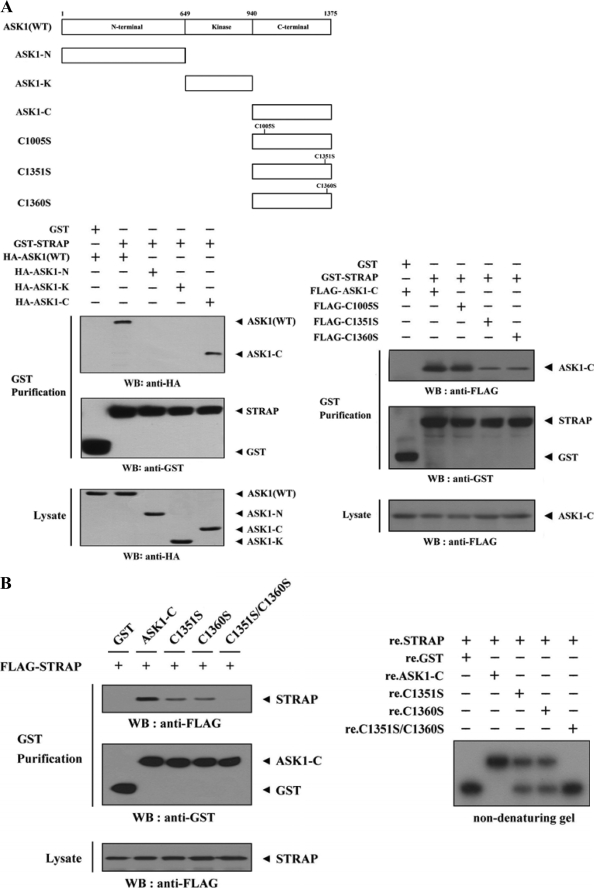
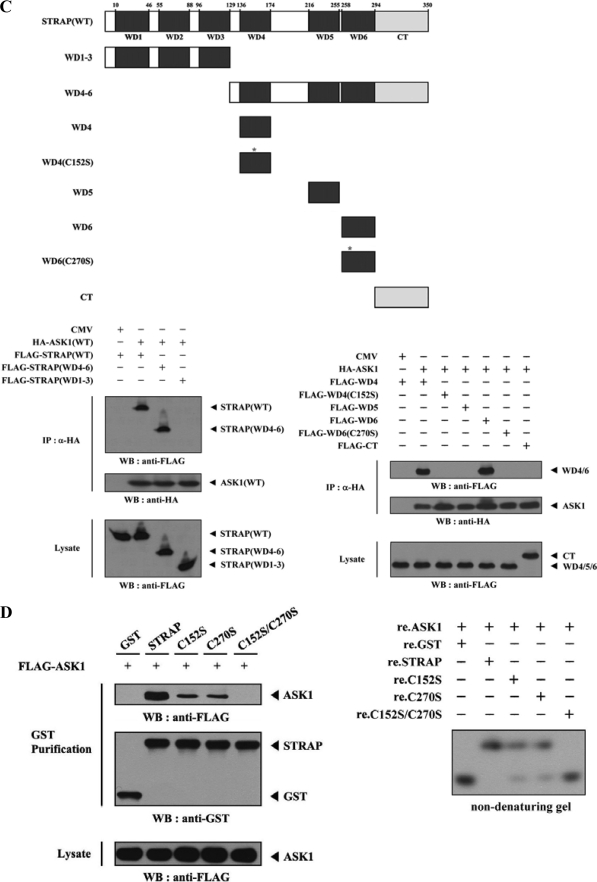
FIGURE 3.
Mapping of the ASK1 and STRAP interaction domains. A and C, schematic structures of wild-type and deletion constructs of ASK1 (A, top) and STRAP (C, top). The numbers indicate the amino acid residues corresponding to the domain boundaries. HEK293 cells transiently transfected with the indicated expression vectors were lysed and then precipitated using glutathione-Sepharose beads (GST Purification) or immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-HA antibody (α-HA) and immunoblotted (WB) with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody to determine the level of ASK1-STRAP complex formation. B, effect of ASK1-C and its substitution mutants (C1351S, C1360S, or C1351S/C1360S) on ASK1-STRAP complex formation. HEK293 cells, transfected with the expression vectors indicated, were lysed, and the GST precipitates were analyzed for complex formation between ASK1 and STRAP by immunoblot analysis with an anti-FLAG antibody (left). For native PAGE (8%) of the ASK1-STRAP complex, in vitro-translated 35S-labeled STRAP was incubated with unlabeled recombinant wild-type and mutant forms of ASK1-C at room temperature for 1 h (right). D, effect of STRAP and its substitution mutants (C152S, C270S, or C152S/C270S) on ASK1-STRAP complex formation. Complex formation between ASK1 and STRAP was analyzed by immunoblot analysis with an anti-FLAG antibody as described for B (left). For native PAGE (8%) of the ASK1-STRAP complex, purified recombinant ASK1 was autophosphorylated, and 2–3 μg was incubated with unlabeled recombinant GST, as a control, or wild-type and mutant forms of STRAP (5 μg of each) as indicated at room temperature for 1 h (right). Experiments were independently performed at least three times with similar results. re., recombinant.