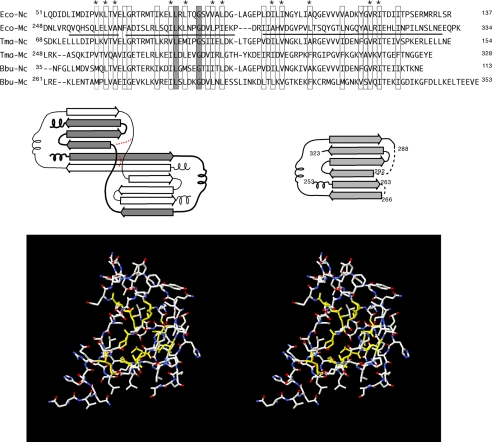
FIGURE 2.
Construction of the FliMC homology model. An alignment of FliN and FliM C-terminal domains is shown in the upper panel. Boxes indicate positions where hydrophobic character is conserved, and asterisks indicate the positions forming the core in both FliN and the homology-modeled FliMC. The solid line under the E. coli C-terminal sequence represents the residues that are included in the FliMC homology model. FliN forms intertwined dimers, with topology sketched in the middle panel. Altered connectivity in two places (indicated in red) allows the FliM peptide to fold as a monomer (consistent with the known properties of FliM, which interacts with FliN to form 1:4 complexes). The homology model has conserved hydrophobic residues at core positions (shown in yellow in the lower panel). Ec-Nc and Ec-Mc, E. coli FliN and FliM C-terminal domains, respectively; Tma-Nc and Tma-Mc, T. maritima FliN and FliM C-terminal domains, respectively; Bbu-Nc and Bbu-Mc, B. burgdorferi FliN and FliM C-terminal domains, respectively.