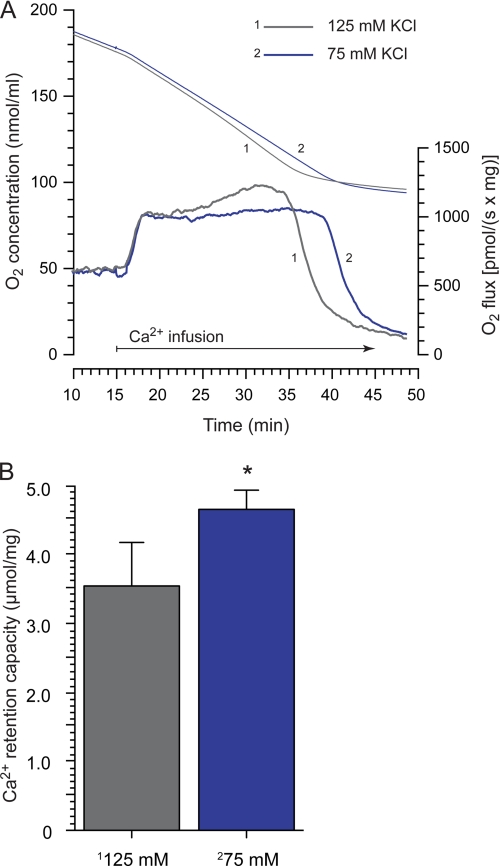
FIGURE 7.
The influence of matrix volume on brain mitochondrial calcium retention. Conditions were as described in Figs. 1 and 2 except that 10 μm bovine serum albumin was present. A, respirometry of mitochondria suspended in standard (125 mm, trace 1) or reduced (75 mm, trace 2) concentrations of KCl during a continuous calcium infusion are shown. The KCl concentration was reduced to lower the medium osmolarity and thereby increase matrix volume. Upper traces are representative examples of changes in O2 concentration, and lower traces depict the corresponding respiration rates (n = 5). The rapid decrease in respiration rate indicates activation of permeability transition. There were no significant differences in basal or calcium-stimulated respiration rates, but there was significant difference in time to respiratory inhibition. B, quantification of CRC of brain mitochondria suspended in 125 or 75 mm KCl media. CRC was calculated as the amount of infused calcium from the start of the elevated respiration rate until start of rapid respiration decrease. The asterisk indicates significant difference between groups.