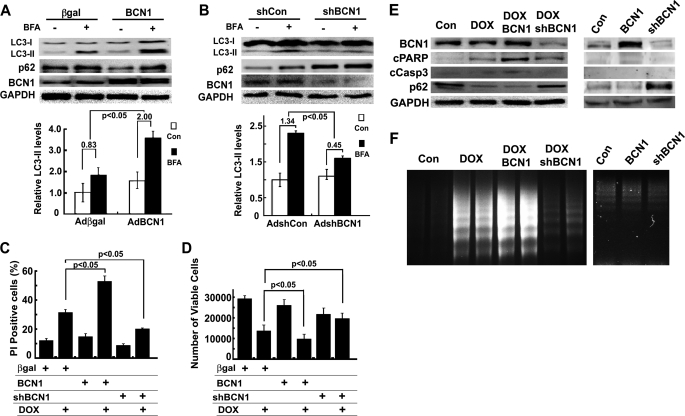
FIGURE 3.
Increased Beclin 1 (BCN1) aggravated DOX toxicity, but knockdown BCN1 reduced it. Cardiomyocytes were infected with AdBCN or AdshBCN for 24 or 48 h and then treated with DOX (1 μm) for another 18 h. Increased Beclin 1 expression accelerated autophagic flux (A, BCN1 2.0 ± 0.34 versus β-galactosidase 0.83 ± 0.30), whereas knocking down Beclin 1 reduced it (B, shBCN1 0.45 ± 0.33 versus shCon 1.34 ± 0.23), as indicated by the difference in protein levels of LC3-II in the absence and presence of BFA. Densitometry data were the mean ± S.E. (n = 6 for BCN1 and 3 for shBCN1) and were analyzed with two-way ANOVA followed by paired Student's t tests. Beclin 1 overexpression exacerbated DOX-induced cell death, and knocking down Beclin 1 reduced it, as determined by PI staining (C), MTT assay (D), cleavage of PARP (cPARP) and caspase 3 (cCasp3, E), and DNA laddering (F). Data in C and D were expressed as the mean ± S.E. and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA (n = 6 for BCN and 3 for shBCN1).