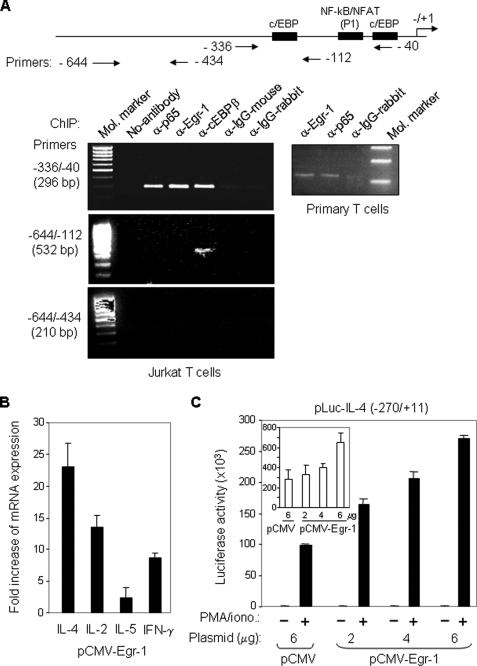
FIGURE 2.
Egr-1 binds to the IL-4 promoter in vivo and activates IL-4 transcription. A, Egr-1 interacts with the human IL-4 promoter in vivo. Jurkat (left) and freshly isolated human peripheral blood T cells (right) were stimulated with PMA (10 ng/ml)/ionomycin (1 μm) or α-CD3 (30 μg/ml)/α-CD28 (5 μg/ml), respectively. After 3 h (Jurkat) and 4 h (primary T cells) of stimulation, cells were subjected to ChIP analysis with the indicated antibodies. A map of the IL-4 promoter showing the location of the primers used for ChIP is also presented. B, ectopic expression of Egr-1 enhances endogenous cytokine expression. Jurkat T cells were transfected with an Egr-1 expression plasmid (pCMV-Egr-1) or with the empty plasmid (pCMV). After overnight recovery of the cells, RNA was prepared, and the expression levels of IL-4, IL-2, IL-5, and IFN-γ were determined by quantitative real time PCR. The results are presented as fold increase in mRNA levels of Egr-1-transfected cells versus empty vector-transfected cells. Results are representative of two independent experiments assayed in triplicate (error bars denote the S.D.). C, ectopic expression of Egr-1 enhances IL-4 promoter activity. The human IL-4 promoter-luciferase reporter construct was co-transfected with either the Egr-1-containing (2–6 μg) or the empty (6 μg) expression vector into Jurkat T cells. After overnight recovery, the transfected cells were split and stimulated with PMA/ionomycin (PMA/iono.) or left unstimulated for 8 h. The promoter activities are given as luciferase activity. Inset, promoter activities in unstimulated conditions are shown magnified. One representative of two independent experiments is shown.