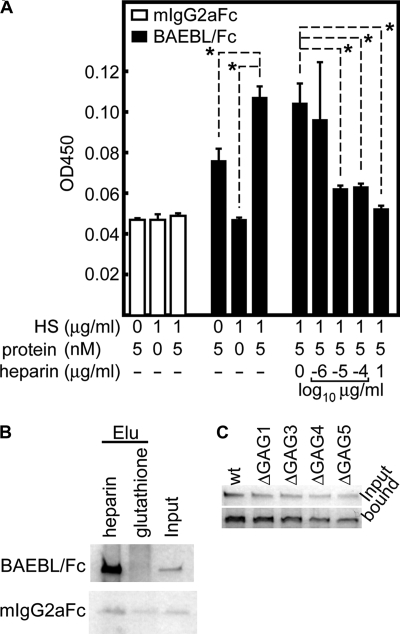
FIGURE 6.
Recombinant BAEBL/Fc binds to purified HS and heparin. A, ELISA-based binding assays of BAEBL to HS. Purified HS was coated onto the wells of an ELISA plate and tested for binding efficiency to the recombinant proteins. The bound protein was detected with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG F(ab′) fragment. Binding inhibition was evaluated by the addition of buffer or 10−6, 10−5, 10−4, or 1 μg/ml soluble heparin to the HS-coated wells immediately before the addition of equal amounts of BAEBL. The optical densities at 450 nm (OD450) are shown as the means of three independent experiments. Error bars, S.E. The asterisks indicate a significant difference (p < 0.01) as determined by t test. B, heparin bead pull-down assays for recombinant proteins. A recombinant protein (500 ng) was incubated with one of two bead types (heparin-agarose and glutathione-Sepharose) for 3.5 h at 4 °C. Eluates (Elu) from the washed beads and 50 ng of untreated protein (Input) were separated by 5–20% gradient SDS-PAGE and subjected to silver staining. C, BAEBL/Fc (wild type (wt)) and four kinds of motif-deleted BAEBL/Fc (ΔGAG1–ΔGAG5) were incubated with heparin-agarose beads. After they were washed, the bound protein and 25 ng of untreated protein (input) were analyzed as described above.