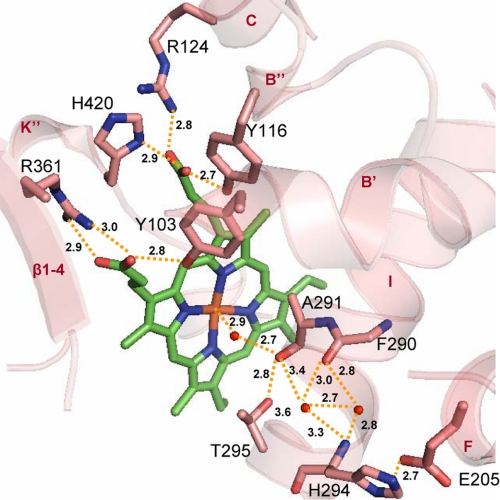
FIGURE 2.
Heme environment in ligand-free Tbb14DM. Heme and surrounding residues are shown in stick representation, H-bonds are indicated with yellow dashes, and the distances (Å) are marked. Upper region, residues interacting with the heme propionates. The A-ring forms H-bonds with Tyr-103 (helix B′) and Arg-361 (β1–4), and the D-ring is supported by Tyr-116 (helix B″), Arg-124 (helix C), and His-420 (helix K″). Lower region, potential I-helix-based proton delivery route. The water molecules included into the H-bond network are presented as small red spheres. The I-helix groove is formed by protrusion of the Ala-291 carbonyl toward the heme and probably modulated by flexible Gly-292. As a result, two helical H-bonds (Phe-290–His-294 and Ala-291–Thr-295) are missing, the peptide carbonyl of Phe-290 being connected through the waters. Ala-291, Gly-292, His-294, and Thr-295 (“the conserved threonine” in the majority of CYP families) are part of the CYP51 I-helix signature (–aGqHTS–). His-294 is the residue specific for the 14DM; the other P450s usually have Asp/Glu in this position. Glu-205 (helix F), which forms a salt bridge with His-294, is also conserved in all 14DM.