FIGURE 3.
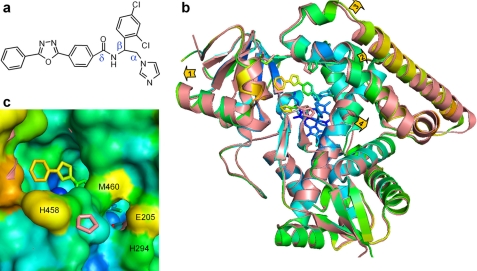
VNI-bound Tbb14DM. a, the chemical structure of VNI. b, superposition of the ligand-free (salmon) and VNI-bound (colored by B-factor) Tbb14DM structures, distal view. The B-factor ranges from blue minimum to red maximum within 17–68 Å2. The heme, VNI, and three residues surrounding the entrance (Ile-45, Pro-210, and His-458) are presented as stick models. Four structural segments where the backbone in all four molecules moves >0.5 Å away from the catalytic core relative to the ligand-free structure are marked with arrows showing the directions of coordinate shifts. 1, N terminus (residues 32–65); 2, BC segment (95–114); 3, FG segment (185–232); and 4, middle part of helix I (288–292). Superimposition of four ligand-free and four VNI-bound molecules can be seen in supplemental Fig. S5. c, enlarged view of the access channel in surface representation; orientation is the same as in b. Some of the heme atoms are seen as blue spheres. The salmon ribbon of the ligand-free structure is partially visible where the shift in the backbone is larger than 1 Å (helices A, F″, and I). The second channel is bordered by helices I (His-294), F (Glu-205), and β4 hairpin (Met-460).