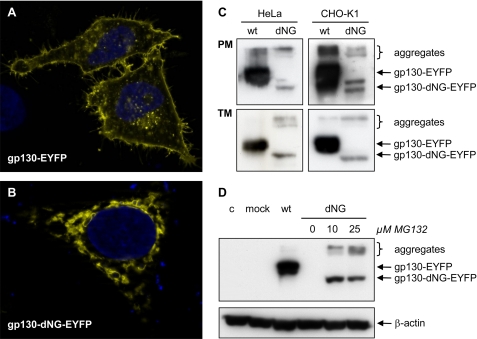
FIGURE 5.
Localization and degradation of gp130-dNG. A and B, fluorescence micrographs of gp130(-dNG)-EYFP in HeLa cells. Whereas wild-type (wt) gp130-EYFP is localized on the cell surface (A), gp130-dNG-EYFP largely remains within the ER·Golgi complex (B). C, Western blots of plasma membrane proteins (PM) and of the complete transmembrane protein fraction (TM) from HeLa and CHO-K1 cells transiently transfected with gp130-EYFP or gp130-dNG-EYFP (detection by anti-EYFP). D, Western blots of denatured whole cell protein extracts from CHO-K1 cells transiently transfected with gp130-EYFP or gp130-dNG-EYFP (detection by anti-EYFP). Proteasome inhibition by MG132 significantly increased protein levels of gp130-dNG-EYFP (normalized by probing the stripped blot membrane with anti-β-actin). Lane 4 (dNG without MG132) does not show a signal due to short exposure time. c, control; mock, only expression vector pcDNA-DEST40. Controls for the experiments shown in C and D included Western blots with anti-gp130 (sc-655, directed against the intracellular domain of gp130) and confirmation of equal protein loading and transfer by Ponceau S staining (data not shown).