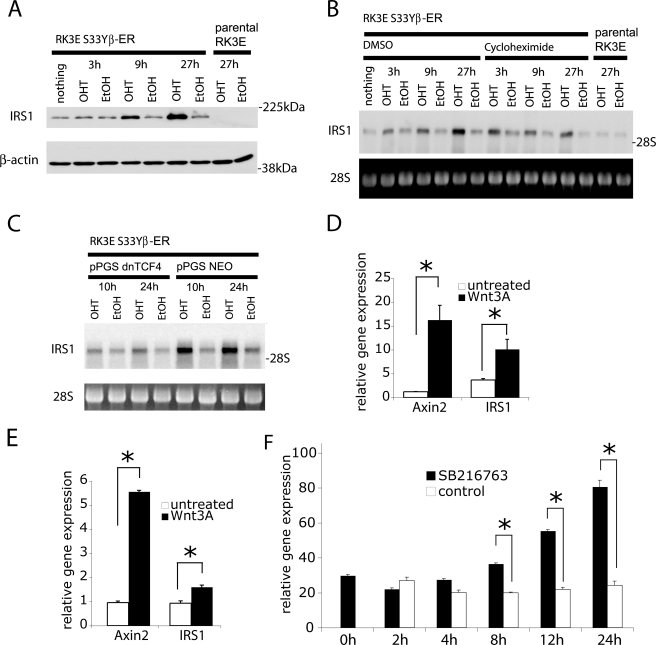
FIGURE 2.
The IRS1 gene is a direct target of β-catenin signaling and IRS1 transcript induction by β-catenin does not require protein synthesis. A, Western blot analysis of a polyclonal RK3E cell line expressing a fusion protein of the hormone binding domain of the murine estrogen receptor (RK3E-S33Y-ER) and a stabilized mutant of β-catenin. IRS1 protein levels were determined at the indicated time points after addition of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT, 500 nm) or a solvent control (Ethanol). B, Northern blot analysis of samples from parental RK3E cells and the RK3E-S33Y-ER cell line stimulated with 4-OHT for the indicated times. Cycloheximide (1.5 μg/ml) or DMSO (i.e. the solvent for cycloheximide) were added 15 min. before treatment with 4-OHT. C, Northern blot analysis of samples from the RK3E-S33Y-ER cell line transduced with a retrovirus to express a dominant-negative mutant of TCF4 (dnTCF4) or control vector. Irs1 mRNA were determined after treatment with 4-OHT or ethanol for 10 and 24 h. In all panels, equal loading is demonstrated by immunoblotting for β-actin or ethidium bromide staining of 28 S ribosomal RNA, respectively. D, IEC6 rat intestinal epithelial cell and E, immortalized ovarian surface epithelium cell lines were treated for 8 h with 50 ng/ml of Wnt3a. Expression of AXIN2 and IRS1 was measured by quantitative PCR and normalized to the expression levels of U6 (D) or HPRT (E), respectively. F, MDAH-2774 cells were treated for the indicated times with the GSK3 inhibitor SB216763. Expression of IRS1 was measured by quantitative PCR and normalized to the expression level of HPRT. Asterisks denote p < 0.05 in Student's t test, and error bars denote S.D.