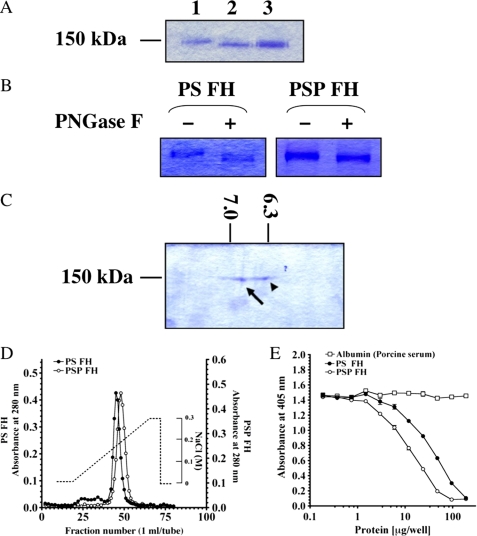
FIGURE 3.
Comparison of molecular weight, pI, heparin-binding activity, and regulation of AP complement activation between FHs from PSP and PS. A, SDS-PAGE of purified FHs from PS and PSP. Three μg each of purified FH from PS (lane 1), PSP (lane 2), and mixed FHs from PSP and PS (lane 3) was loaded on SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. B, deglycosylation of both FHs by PNGase F. Purified FHs from PS and PSP were treated with PNGase F (lanes 2 and 4) or not-treated with PNGase F (lanes 1 and 3). These samples were electrophoresed on 7.5% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. C, two-dimensional electrophoresis of purified FHs from PSP and PS. A mixture of 4 μg of each FH from PSP and PS was loaded and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250. pI values of FH from PSP (arrow) and PS (arrowhead) were 6.90 and 6.35, respectively. D, comparison of heparin-binding activities of PSP and PS FHs. Approximately 3 mg of purified FH from PSP (open circles) and the same amount of purified FH from PS (filled circles) were applied onto a HiTrapTM heparin column. Each protein was eluted with a linear gradient from 0 to 0.3 m NaCl. Similar results were obtained from at least three separate experiments. E, AP complement regulatory activities of FHs from PSP (open circles) and PS (filled circles). The assay was carried out on an LPS-coated microtiter plate. Porcine albumin (open squares) was used as a negative control. Similar results were obtained from at least three separate experiments. Each value is the mean ± S.E. from triplicate experiments.