Table 4.
Reaction of Various Allyl Enol Carbonatesa
| entry | substrate | product | yieldb eec |
Lit,d yield, ee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 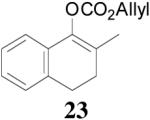 |
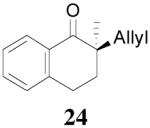 |
88% 99.7% ee R-(+) e |
99% 88% ee R-(+) |
| 2 | 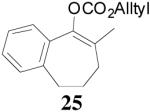 |
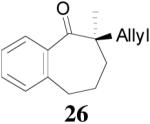 |
94% 91% ee f (−) |
90% 6% ee (+) |
| 3 | 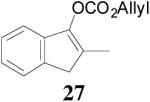 |
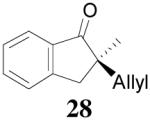 |
98% 76%ee (+) |
79% 38% ee (+) |
| 4 | 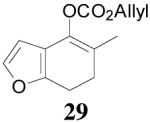 |
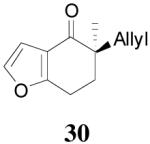 |
64% 82% ee (+) |
59% 45% ee (−) |
| 5 | 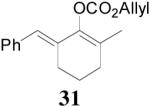 |
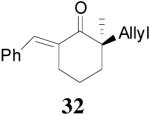 |
99% 95% ee (+) |
98% 82% ee (−) |
All reactions were performed on a 0.3 mmol scale at 0.1 M in toluene at 23 °C for 20 h using 2.5 mol% 20 and 5.5 mol% ligand (R,R)-L4.
Isolated yields.
Ee values were determined by HPLC on a chiral stationary phase.
Conditions used were 2.5 mol% [(η3-C3H5)PdCl]2, 5.0 mol% (S,S)-L1, 2.0 equiv LDA, 1.0 equiv Me3SnCl, DME, r.t.10
The absolute configuration and the sign of the optical rotation ([α]D) of the product.9a
Ee was determined by GC on a chiral stationary phase.
