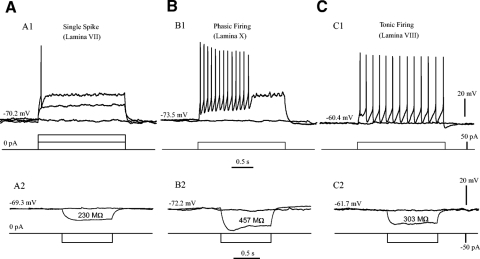
Fig. 5.
Three types of EGFP+ neurons. The EGFP+ neurons were classified into 3 types based on their firing patterns (A1–C1, top) in response to depolarizing step currents (2 s, 50 pA for each step; A1–C1, bottom). The passive membrane responses (A2–C2, top) to hyperpolarizing step currents (1 s, −50 pA for each step; A2–C2, bottom) were used to calculate input resistance by Ohm law. A: cells of single spike (type 1). A1: 2 step currents were injected into a type 1 cell and only one single spike was elicited by the 2nd step (2 s, 100 pA). A2: a hyperpolarizing step current (1 s, −50 pA) was injected into the same cell, and the voltage deflection was used to calculate the Rin (230 MΩ). B: cells of phasic firing (type 2). B1: a 50-pA step current evoked a brief firing in a type 2 cell for ∼0.6 s. B2: the cell membrane potential was hyperpolarized by a −50-pA step current, and the Rin was calculated as 457 MΩ in this cell. C: cells of tonic firing (type 3). C1: the tonic firing in a type 3 cell was evoked by a 50 pA depolarizing step current. C2: the hyperpolarization of membrane potential was produced by a −50-pA step current. Rin = 303 MΩ in this cell.