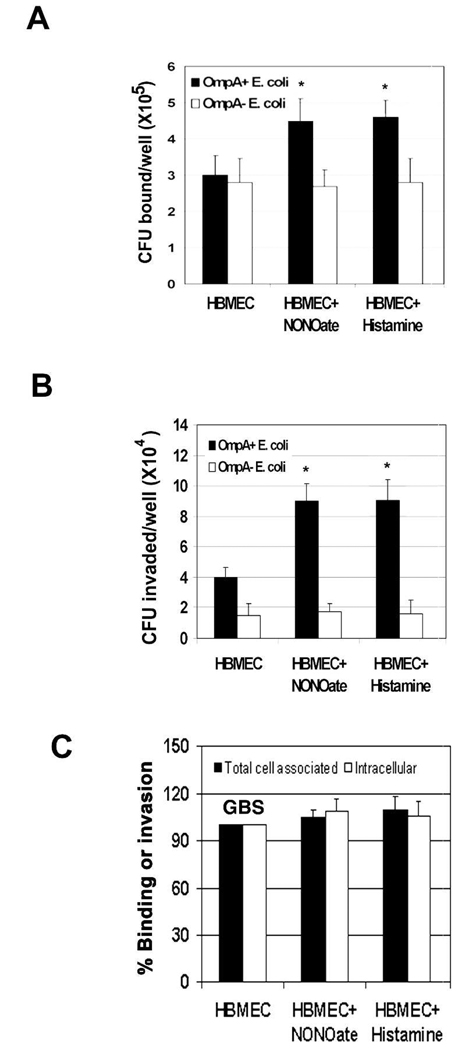
Fig. 5. The inducers of NO production increased the invasion of E. coli in HBMEC.
Confluent monolayers of HBMEC were treated with NONOate or histamine for 1 h prior to the addition of E. coli (A and B) or GBS (C). Total bacteria bound to or invaded the monolayers was determined as described in the methods section. The data were presented as the number of CFU bound or invaded per well in case of E. coli or percent binding/invasion being taken the binding/invasion of GBS in control HBMEC as 100%. The experiments were performed at least three times in triplicate and the error bars represent SD. The increase in binding or invasion was significantly higher in NONOate or histamine treated HBMEC in comparison to control HBMEC (*P<0.001 by Student’s t test).