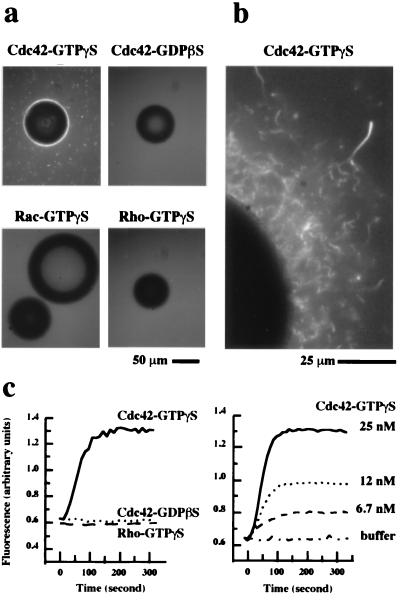
Figure 1.
Assays for Cdc42-induced actin polymerization in Xenopus high speed supernatants. (a) Actin polymerization was monitored by the visual assay in which rhodamine actin (1 μM) was used to follow actin polymerization by fluorescence microscopy. The extracts were stimulated with glutathione Sepharose beads coated with GST-Cdc42, GST-Rac, or GST-Rho (2 mg of protein/ml packed beads) charged with GTPγS or GDPβS. Bright fluorescence around the bead indicated polymerized actin. (b) A high magnification view of actin polymerization around a bead coated with GST-Cdc42-GTPγS. (c) Kinetics of actin polymerization in high speed supernatants as monitored by the pyrene actin assay in which fluorescence increase indicates the formation of actin filaments. Extracts were stimulated by Cdc42-GTPγS (25 nM), Cdc42-GDPβS (25 nM), and Rho-GTPγS (50 nM) (left) or by Cdc42-GTPγS at different concentrations (right).