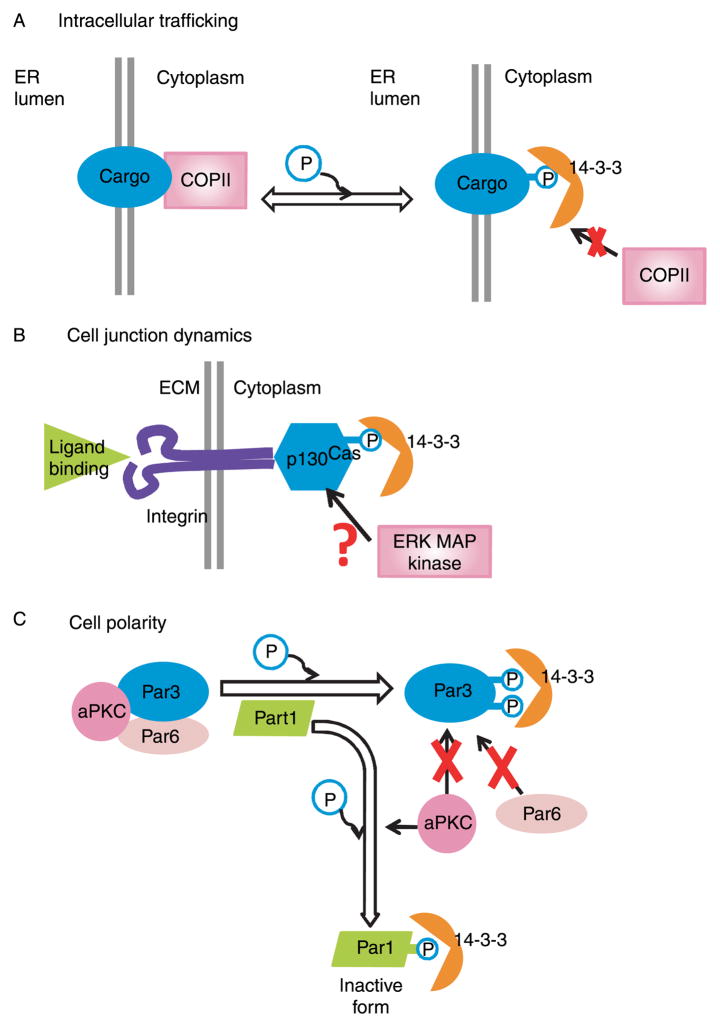
Figure 2.
The three possible regulatory functions of 14-3-3 in the testis. (A) Effects on intracellular trafficking. 14-3-3 binding modulates endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transportation by masking the COPII (or COPI) binding sites on cargo proteins. (B) Effects on cell-junction dynamics. 14-3-3 participates in the integrin-activated signaling pathways via p130Cas. (C) Effects on cell polarity. Par1 catalyzes the phosphorylation of Par3, leading to 14-3-3 binding that inhibits the formation of Par3/Par6/aPKC complex. In turn, Par1 can be phosphorylated by aPKC (atypical protein kinase C) and bound with 14-3-3 as inactive form.