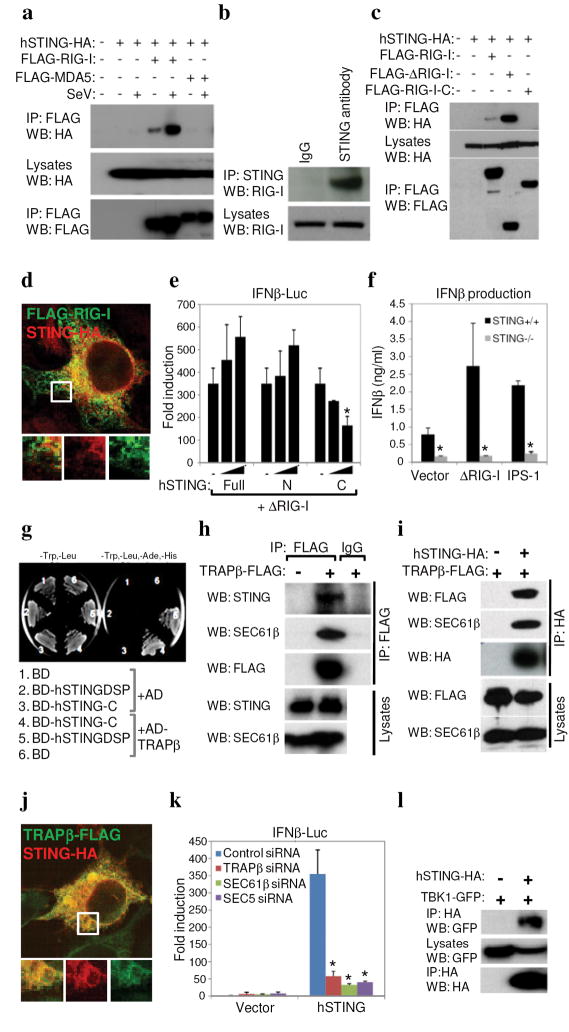
Fig 4. STING associates with the translocon.
a. 293T cells were co-transfected with HA-STING, FLAG-RIG-I or MDA5 and infected with SeV (MOI 1). Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) and immunoblotted (IB) using antibodies to HA or FLAG. b. Endogenous hSTING associates with RIG-I in HUVECs. c. ΔRIG-I (aa1-284) and not RIG-I-C (aa218-925) associates with STING in co-transfected 293T cells. d. Confocal image of 293T cells co-transfected with tagged STING and RIG-I. e. 293T cells were co-transfected with control vector (−) or increasing amounts of full-length, amino (aa1-230) or carboxyl (aa173-379) STING and ΔRIG-I, and IFNβ-Luc was measured. f. Control or STING −/− MEFs were transfected with ΔRIG-I (aa1-284) or IPS-1 and IFNβ was measured by ELISA. g. BD-hSTING-C interacts with Ssr-2/TRAPβ (AD-hTRAPβ) in yeast-two hybrid screening (BD-hSTINGΔSP, amino acids 36-369; BD-hSTING-C amino acids 173-379). h. HEK 293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged TRAPβ and endogenous STING or Sec61β measured by immunoblot. i. STING and TRAPβ were co-transfected HEK 293 cells and analysis carried out as in (h). j. Co-localization of STING and TRAPβ in 293T cells. k. RNAi to TRAPβ, SEC61β or Sec5 in HEK 293 cells ablates STING signaling. l. HA-STING associates with GFP-TBK-1 in co-transfected HEK 293 cells. Asterisks indicate significant difference (P < 0.05) as determined by Student’s t-test. Error bars; +/− s.d.