Table 1.
Optimization of Pd-catalyzed silylation reactions.a
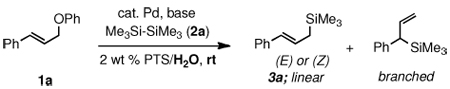 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | catalyst | base (equiv) | convn (%)b | l:bb | E:Zb |
| 1 | PdCl2(PPh3)2 | Et3N (6) | 44 | 25:1 | 19:1 |
| 2 | PdCl2(DtBPF) | Et3N (6) | 40 | 7:1 | 25:1 |
| 3 | PdCl2(DiPPF) | Et3N (6) | 60 | 24:1 | 25:1 |
| 4 | PdCl2(DPEphos) | Et3N (6) | 100 (91)c | 25:1 | 10:1 |
| 5 | PdCl2(DPEphos) | Et3N (4) | 95 | 25:1 | 10:1 |
| 6 | PdCl2(DPEphos) | Et3N (2) | 95 | 25:1 | 10:1 |
| 7 | PdCl2(DPEphos) | aminesd | 0 | ||
| 8 | PdCl2(DPEphos) | K2CO3 (3) | 73 | 25:1 | 13:1 |
Reaction conditions: 1a (1.0 equiv, 0.25 mmol), 2a (1.5 equiv), catalyst (3 mol %), base, 2 wt % PTS/H2O (1.5 mL), rt, 20 h.
Determined by GCMS and 1H NMR.
Isolated yield.
nBu3N and EtiPr2N were used.
