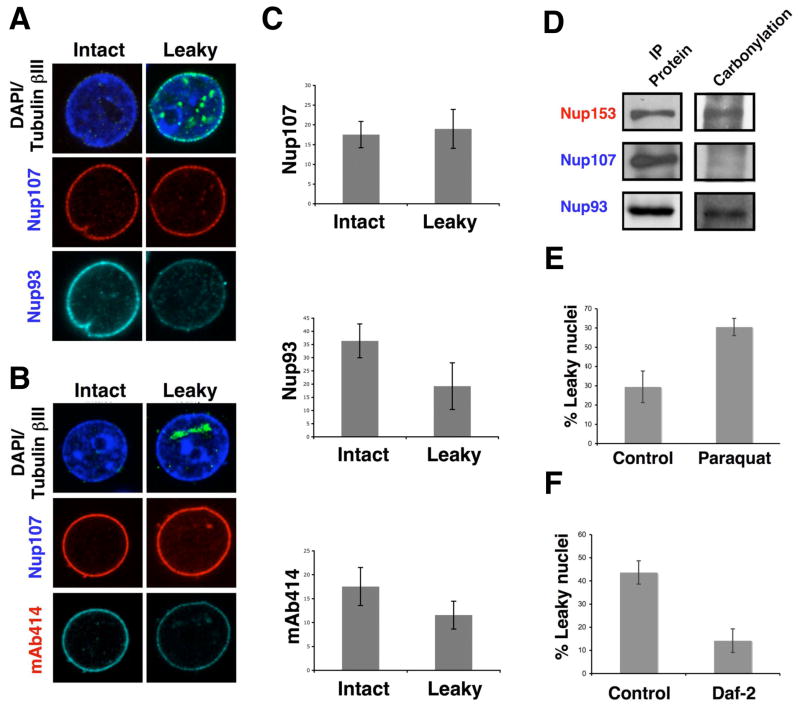
Figure 7. Nuclei with increase permeability show deteriorated NPCs.
(A). Nuclei were isolated from brains of old (28 months) rats, fixed and stained with antibodies against tubulin bIII and the scaffold nucleoporins Nup107 and Nup133. The staining of intact and leaky nuclei (the latter identified by the intranuclear accumulation of intranuclear tubulin bIII) was compared. (B) Intact and leaky nuclei isolated from old rat brains were stained with tubulin bIII, Nup107 and the mAb414 antibody. Intact and leaky nuclei were compared as described in (A). (C) The fluorescent intensity of the nuclei stained in (A) and (B) was quantified using Image J. (D) Total protein extracts were prepared from brains of old rats and nucleoporins were immunoprecipitated (IP) using specific antibodies. The IP proteins were treated with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to derivatize carbonyl groups to 2.4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (DNP-hydrazone) The DNP-derivatized proteins were detected by western blot using an anti-DNP antibody. (E) C. elegans SS104 worms on day 1 of adulthood were transfer to plates containing bacteria and buffer (Control) or Paraquat (0.5mM). On day 6 nuclei were isolated from worms and nuclear permeability was analyzed using the 70 and 500 kDa dextrans assay and quantified using Photoshop CS3 Extended. (F) SS104 adult day 1 worms were grown in bacteria expressing empty vector (Control) or daf-2 RNAi (Daf-2) for 8 days. Nuclei were isolated from worms and nuclear permeability was analyzed as in (D).