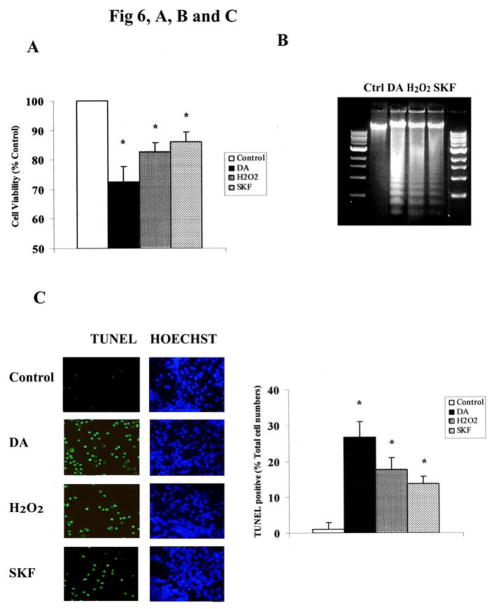
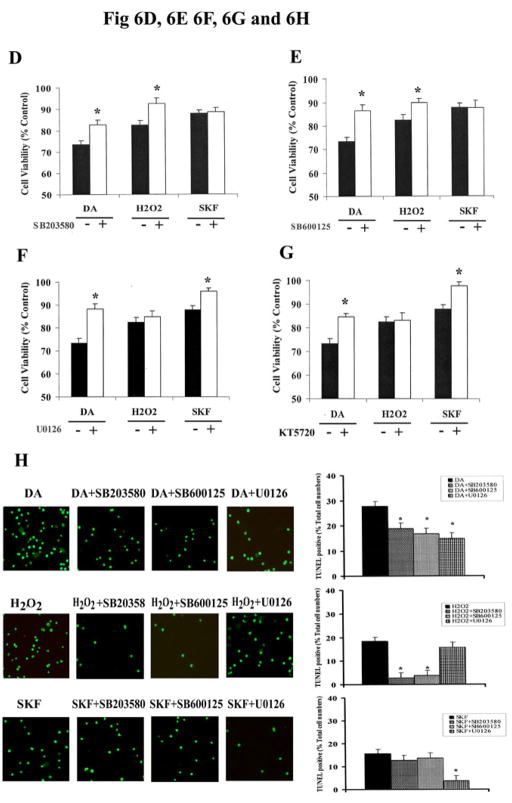
Fig. 6. MAPKs mediate DA-induced neuronal apoptotic death in striatal neurons.
A. Exposure of striatal neurons to either 10μM of DA, H2O2 or SKF R-38393 for 24 h. Cell viability (A), DNA fragmentation (B) and TUNEL staining (C) was conducted as described in Experimental Procedures. Values shown are the average ± S.E.M (n=5). p<0.05 (*), represents the result of paired Student’s t test with 8 degrees of freedom for the corresponding control group. In panels D, E, F and G, striatal neurons were exposed to 10 μM of DA, H2O2 or SKF R-38393 for 24 h, occurred in the presence (+) or absence (−) of either the selective p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (D), or the selective JNK inhibitor SB600125 (E), or the selective MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 (F), or the selective PKA inhibitor KT5720 (G). Neuronal viability was measured by the MTT cell viability assay. Kinase inhibitors (1 μM each) were added 15 min before treating the neurons. In panel H. Striatal neurons were pretreated for 15 min with vehicle or with 1 μM of SB203580, SB600125 or U0126, then treated with 10 μM of either DA, H2O2 or SKF R-38393 for 24 h. TUNEL staining was conducted. In bar graph, data are expressed relative to control, and represent as the average ± S.E.M of three independent experiments (n=3) for each treatment. p<0.05 (*), represents the result of paired Student’s t test with 4 degrees of freedom for the corresponding DA, H2O2 or SKF R-38393 treatment group.