Table 1.
Selected data from sulfonylation catalyst screen.a
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Catalyst | Temp. | i+1 | i+2 | i+3 | i+4 | erb |
| 1 | 3 | 23 °C | Hyp(But) | Sp5 | Tyr(But) | Phe | 67.5:32.5 |
| 2 | 4 | 23 °C | Hyp(But) | Sp5 | Leu | Phe | 84.5:15.5 |
| 3 | 5 | 23 °C | Hyp(But) | Aib | Leu | Phe | 83.5:16.5 |
| 4 | 6 | 23 °C | Pro | Aib | Leu | Phe | 76.5:23.5 |
| 5 | 4 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | Sp5 | Leu | Phe | 89.0:11.0 |
| 6 | 5 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | Aib | Leu | Phe | 87.0:13.0 |
| 7 | 7 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | D-Val | Leu | Phe | 92.5:7.5 |
| 8 | 8 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | Val | Leu | Phe | 60.0:40.0 |
| 9 | 9 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | Sp5 | Leu | D-Phe | 91.5:8.5 |
| 10 | 10 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | Sp5 | Leu | ----- | 97.0:3.0 |
| 11 | 11 | 0 °C | Hyp(But) | D-Val | Leu | ----- | 95.5:4.5 |
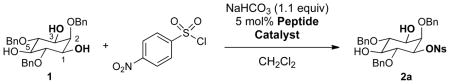
Reactions were run with 1.0 equiv 2,4,6-tribenzyl-myo-inositol (1) and 1.0 equiv 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride. Reactions were run under a common set of conditions, and conversions were found to be approximately 10%, with some variation. The issue of secondary kinetic resolution was addressed subsequently (vide infra).
All enantiomer ratios were measured using chiral HPLC.
