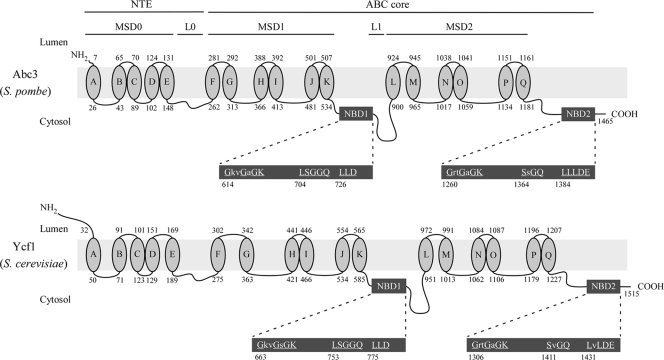
FIG. 1.
Structural features of Abc3 and its close homologue from S. cerevisiae Ycf1. Topological models of the S. pombe Abc3 (top) and S. cerevisiae Ycf1 (bottom) proteins are shown. The N-terminal extension (NTE) includes five membrane spans (denoted as MSD0; ovals A to E) and a cytosolic loop (L0). The ABC core domain consists of two homologous halves, each containing a transmembrane domain (denoted as MSD1 or MSD2) composed of six membrane spans (ovals F to K or ovals L to Q), and a nucleotide binding domain (denoted as NBD1 or NBD2). The halves are joined by a linker region (L1). NBD1 and NBD2 (enlarged dark gray boxes) contain residues that are found in other ABC transporters. Highly conserved residues are both underlined and in capital letters. The amino acid sequence numbers refer to the position relative to the first amino acid of each protein.