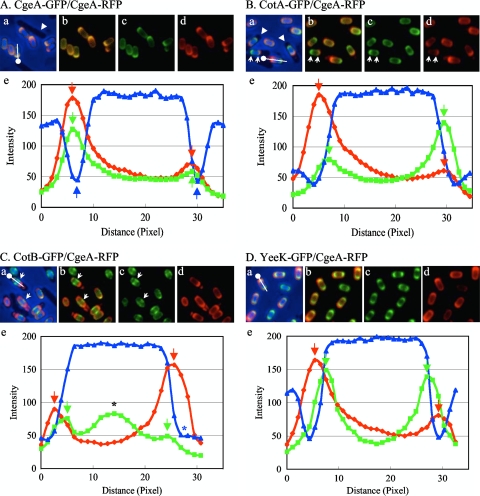
FIG. 1.
Fluorescence localization of coat protein-GFP and -RFP fusions and plots of fluorescence and phase-contrast intensities along the long axis of the spore. Strains possessing CgeA-RFP and CgeA-GFP (A), CotA-GFP (B), CotB-GFP (C), or YeeK-GFP (D) were induced to sporulate by nutrient exhaustion. Merged GFP and RFP fluorescence and blue phase-contrast images (a), merged GFP and RFP fluorescence images (b), GFP fluorescence images (c), and RFP fluorescence images (d) are shown. The dot with the line in each panel a indicates the long axis of the spore for which plots of fluorescence and phase-contrast intensities are shown in the corresponding panel e. The dot in panel a indicates the side of distance zero in panel e. Green and red arrows in panels e indicate peaks of GFP and RFP fluorescence intensities, respectively. (A) Blue arrows in panel e indicate negative peaks of phase-contrast intensity. The white arrowhead in panel a indicates a nonsporulating cell. (B) White arrowheads in panel a indicate mother cells. White arrows indicate opposite abundance patterns of CotA-GFP and CgeA-RFP. (C) White arrows indicate a ring- or spiral-like structure of CotB-GFP. The black asterisk in panel e indicates the peak of fluorescence intensity of the ring- or spiral-like structure of CotB-GFP. The blue asterisk in panel e indicates the absence of a negative peak of phase-contrast intensity.