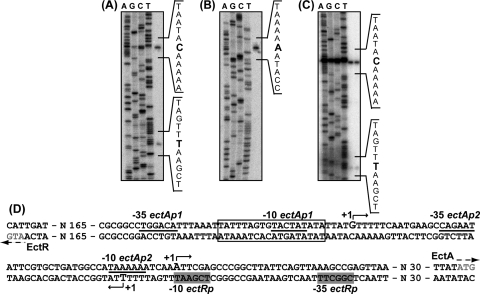
FIG. 3.
Determination of transcriptional start sites for the ectABC-ask operon and the ectR1 gene. Primer extension analyses were carried out with total RNA prepared from M. alcaliphilum 20Z cells (A and B) and E. coli cells (C) using primers complementary to the ectA (A and C) and ectR1 (B) genes as indicated in Materials and Methods. Primer-extended products were separated by electrophoresis under denaturing conditions alongside the products of sequencing reactions with the same primers. (D) Sequence of the ectR1-ectA intergenic region. Bent arrows indicate the transcriptional initiation sites of the ectABC-ask operon and the ectR1 gene. Putative promoter elements (−10 and −35 boxes) for the ectAp1 and ectAp2 promoters of the ectABC-ask operon are underlined. Putative −10 and −35 elements for the promoter of the ectR1 gene are shaded. The translational start codons for the ectA and ectR1 genes are indicated by arrows. The inverted repeat of the EctR1 binding site (see below) is boxed.