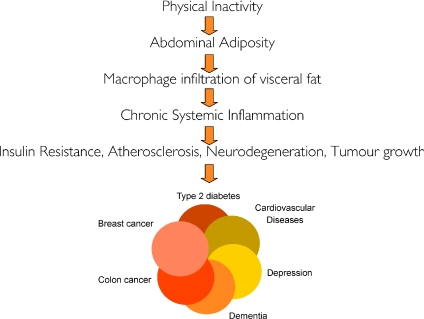
Figure 2.
Hypothesis: Physical inactivity leads to accumulation of visceral fat and consequently to the activation of a network of inflammatory pathways, which promotes development of insulin resistance, atherosclerosis, neurodegeneration, and tumour growth, leading to the development of ‘the diseasome of physical inactivity’