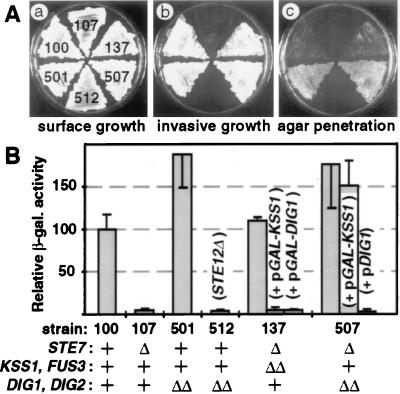
Figure 2.
Dig1 and Dig2 cooperate with Kss1 to inhibit invasive growth. (A) Loss of DIG1 and DIG2 enhance haploid invasive growth. Strain JCY100 (MATa STE+ DIG+) and its otherwise isogenic derivatives, JCY107 (ste7Δ), JCY137 (ste7Δ kss1Δ fus3Δ), JCY501 (dig1Δ dig2Δ), JCY512 (dig1Δ dig2Δ ste12Δ), and YLB507 (ste7Δ dig1Δ dig2Δ), were streaked onto YPD plates and assayed for surface growth (a), invasive growth (b), and agar penetration (c) after 3 days at 30°C. (B) Effect of Kss1 or Dig1 overproduction on expression of the FRETy1-lacZ reporter: Dig1 and Dig2 are required for Kss1-imposed repression. The strains described in A were transformed with plasmid YEpU-FTyZ or YEpL-FTyZ. JCY137 was also transformed with either YCpLG-KSS1 (pGAL-KSS1) or pGAL-DIG1, for overproduction of Kss1 or Dig1, respectively, from the GAL1 promoter. YLB507 was also transformed with YCpLG-KSS1 (pGAL-KSS1) or pDIG1, for overproduction of Kss1 or endogenous-level expression of Dig1, respectively. Strains were grown on plates containing 2% galactose and 0.2% sucrose as the carbon source for 24 hr at 30°C, and β-galactosidase specific activity was measured as in Fig. 1. Values are normalized to that observed for JCY100 (11, 300 nmol per min per mg of protein).